PHAROS¶
OPNFV Community Lab Infrastructure¶
1. Pharos Project Information¶
1.1. Introduction¶
The Pharos Project deals with developing an OPNFV lab infrastructure that is geographically and technically diverse. This will greatly assist in developing a highly robust and stable OPNFV platform. Community labs are hosted by individual companies and there is also an OPNFV lab hosted by the Linux Foundation that has controlled access for key development and production activities. The Pharos Specification defines a “compliant” deployment and test environment. Pharos is responsible for defining lab capabilities, developing management/usage policies and process; and a support plan for reliable access to project and release resources. Community labs are provided as a service by companies and are not controlled by Pharos however our goal is to provide easy visibility of all lab capabilities and their usage at all-times.
A requirement of Pharos labs is to provide bare-metal for development, deployment and testing. This is resource intensive from a hardware and support perspective while providing remote access can also be very challenging due to corporate IT policies. Achieving a consistent look and feel of a federated lab infrastructure continues to be an objective. Virtual environments are also useful and provided by some labs. Jira is currently used for tracking lab operational issues as well as for Pharos project activities.
Future lab capabilities are currently focused on:
- Automatic resource provisioning
- Dashboards (for capability and usage)
- Virtual Labs for developer on-boarding
1.2. Project Communication¶
- Pharos page
- Pharos project Wiki
- Pharos Planning
- Pharos Jira
- Bi-weekly Pharos meeting
- Weekly INFRA WG meeting
- Weekly coordination meeting for Test related projects
- IRC: freenode.net #opnfv-pharos
- Mailing List: use opnfv-tech-discuss and tag your emails with [Pharos] in the subject for filtering
1.3. Project Release Artifacts¶
1.4. Pharos Lab Process¶
- Process for requesting lab access and support https://wiki.opnfv.org/display/pharos/Pharos+Rls+B+Support
- Pharos Lab Governance and Policies https://wiki.opnfv.org/display/pharos/Pharos+Policies
- Status of Community labs https://wiki.opnfv.org/display/pharos/#PharosHome-Overview
1.5. Current Labs¶
An interactive map of OPNFV lab locations, lab owners and other lab information is maintained on the Pharos Wiki
2. Pharos Specification¶
The Pharos Specification provides information on Pharos hardware and network requirements
2.1. Pharos Compliance¶
The Pharos Specification defines a hardware environment for deployment and testing of the Brahmaputra platform release. The Pharos Project is also responsible for defining lab capabilities, developing management/usage policies and process; and a support plan for reliable access to project and release resources. Community labs are provided as a service by companies and are not controlled by Pharos however our objective is to provide easy visibility of all lab capabilities and their usage at all-times.
Pharos lab infrastructure has the following objectives: - Provides secure, scalable, standard and HA environments for feature development - Supports the full Brahmaputra deployment lifecycle (this requires a bare-metal environment) - Supports functional and performance testing of the Brahmaputra release - Provides mechanisms and procedures for secure remote access to Pharos compliant environments for
OPNFV community
Deploying Brahmaputra in a Virtualized environment is possible and will be useful, however it does not provide a fully featured deployment and realistic test environment for the Brahmaputra release of OPNFV.
The high level architecture is outlined in the following diagram:
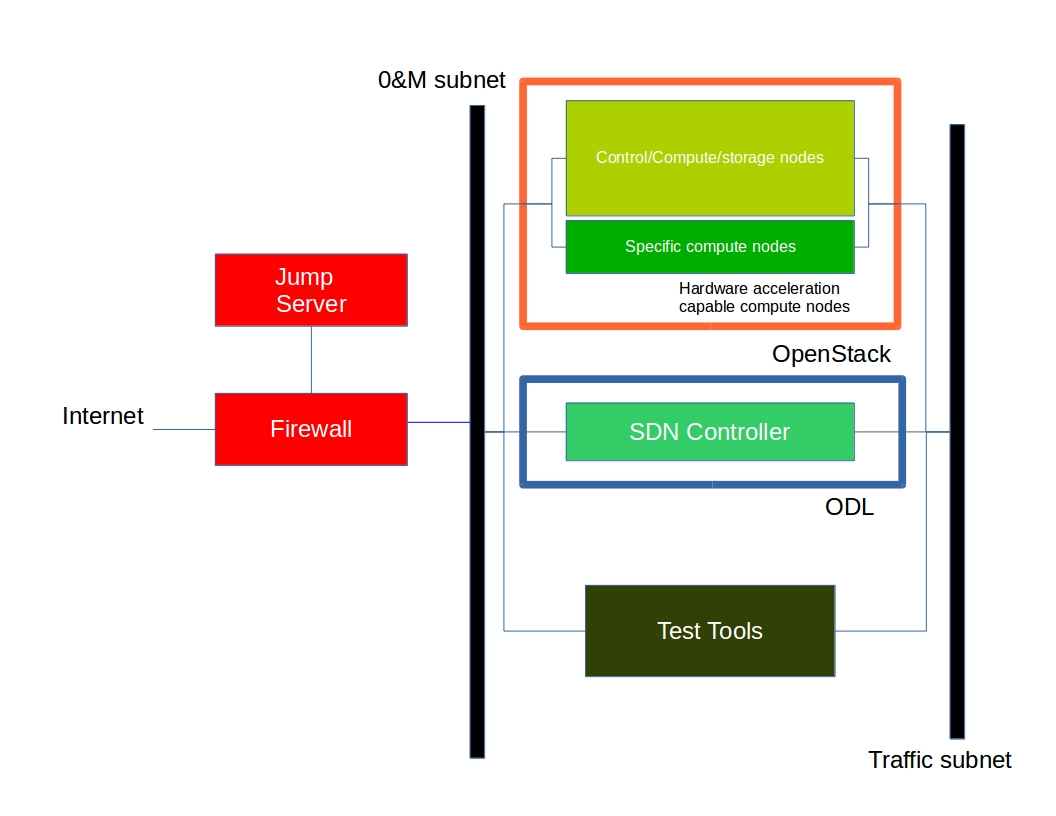
2.2. Hardware¶
A pharos compliant OPNFV test-bed provides:
- One CentOS 7 jump server on which the virtualized Openstack/OPNFV installer runs
- In the Brahmaputra release you may select a variety of deployment toolchains to deploy from the jump server.
- 5 compute / controller nodes (BGS requires 5 nodes)
- A configured network topology allowing for LOM, Admin, Public, Private, and Storage Networks
- Remote access as defined by the Jenkins slave configuration guide
http://artifacts.opnfv.org/brahmaputra.1.0/docs/opnfv-jenkins-slave-connection.brahmaputra.1.0.html
Servers
CPU:
- Intel Xeon E5-2600v2 Series or newer
- AArch64 (64bit ARM architecture) compatible (ARMv8 or newer)
Firmware:
- BIOS/EFI compatible for x86-family blades
- EFI compatible for AArch64 blades
Local Storage:
Below describes the minimum for the Pharos spec, which is designed to provide enough capacity for a reasonably functional environment. Additional and/or faster disks are nice to have and mayproduce a better result.
- Disks: 2 x 1TB HDD + 1 x 100GB SSD (or greater capacity)
- The first HDD should be used for OS & additional software/tool installation
- The second HDD is configured for CEPH object storage
- The SSD should be used as the CEPH journal
- Performance testing requires a mix of compute nodes with CEPH (Swift+Cinder) and without CEPH storage
- Virtual ISO boot capabilities or a separate PXE boot server (DHCP/tftp or Cobbler)
Memory:
- 32G RAM Minimum
Power Supply
- Single power supply acceptable (redundant power not required/nice to have)
2.3. Networking¶
Network Hardware
- 24 or 48 Port TOR Switch
- NICs - Combination of 1GE and 10GE based on network topology options (per server can be on-board or use PCI-e)
- Connectivity for each data/control network is through a separate NIC. This simplifies Switch Management however requires more NICs on the server and also more switch ports
- BMC (Baseboard Management Controller) for lights-out mangement network using IPMI (Intelligent Platform Management Interface)
Network Options
- Option I: 4x1G Control, 2x10G Data, 48 Port Switch
- 1 x 1G for lights-out Management
- 1 x 1G for Admin/PXE boot
- 1 x 1G for control-plane connectivity
- 1 x 1G for storage
- 2 x 10G for data network (redundancy, NIC bonding, High bandwidth testing)
- Option II: 1x1G Control, 2x 10G Data, 24 Port Switch
- Connectivity to networks is through VLANs on the Control NIC
- Data NIC used for VNF traffic and storage traffic segmented through VLANs
- Option III: 2x1G Control, 2x10G Data, 2x10G Storage, 24 Port Switch
- Data NIC used for VNF traffic
- Storage NIC used for control plane and Storage segmented through VLANs (separate host traffic from VNF)
- 1 x 1G for lights-out mangement
- 1 x 1G for Admin/PXE boot
- 2 x 10G for control-plane connectivity/storage
- 2 x 10G for data network
Documented configuration to include:
- Subnet, VLANs (may be constrained by existing lab setups or rules)
- IPs
- Types of NW - lights-out, public, private, admin, storage
- May be special NW requirements for performance related projects
- Default gateways
Sample Network Drawings
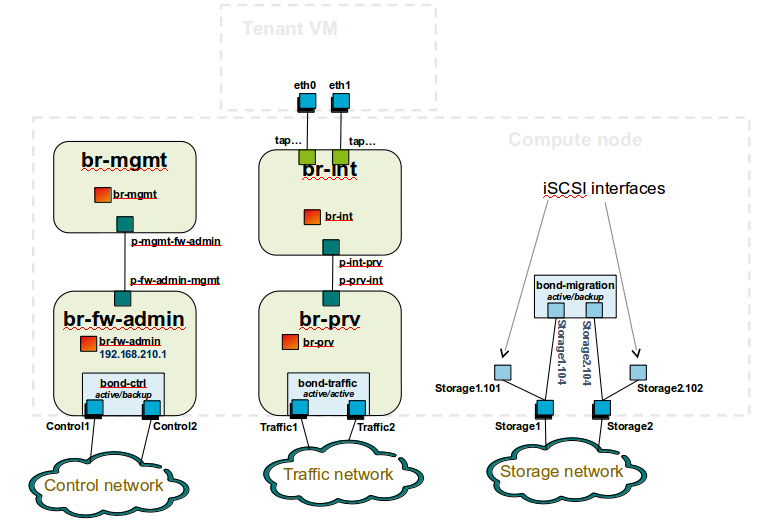
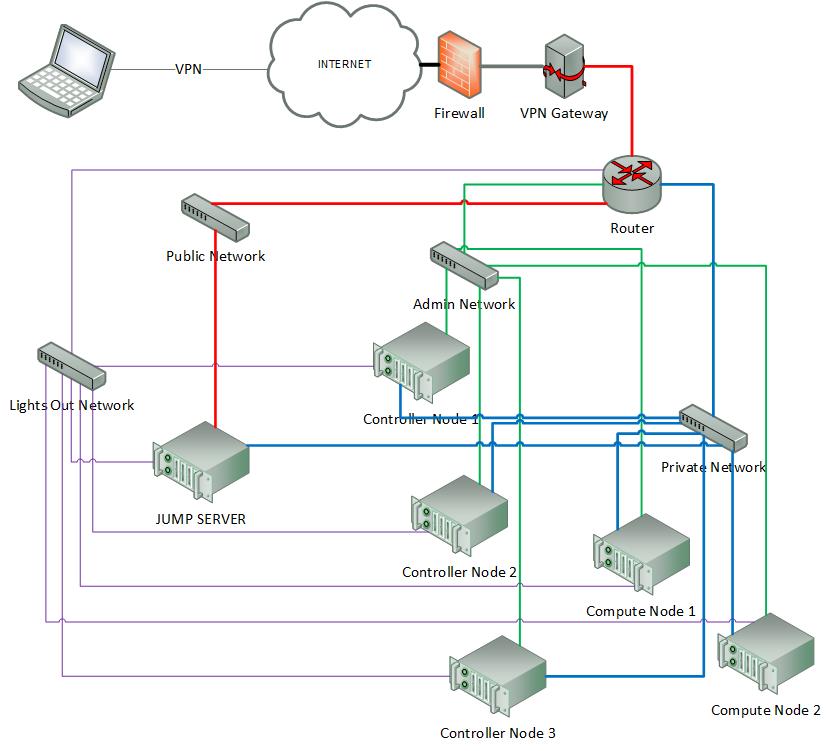
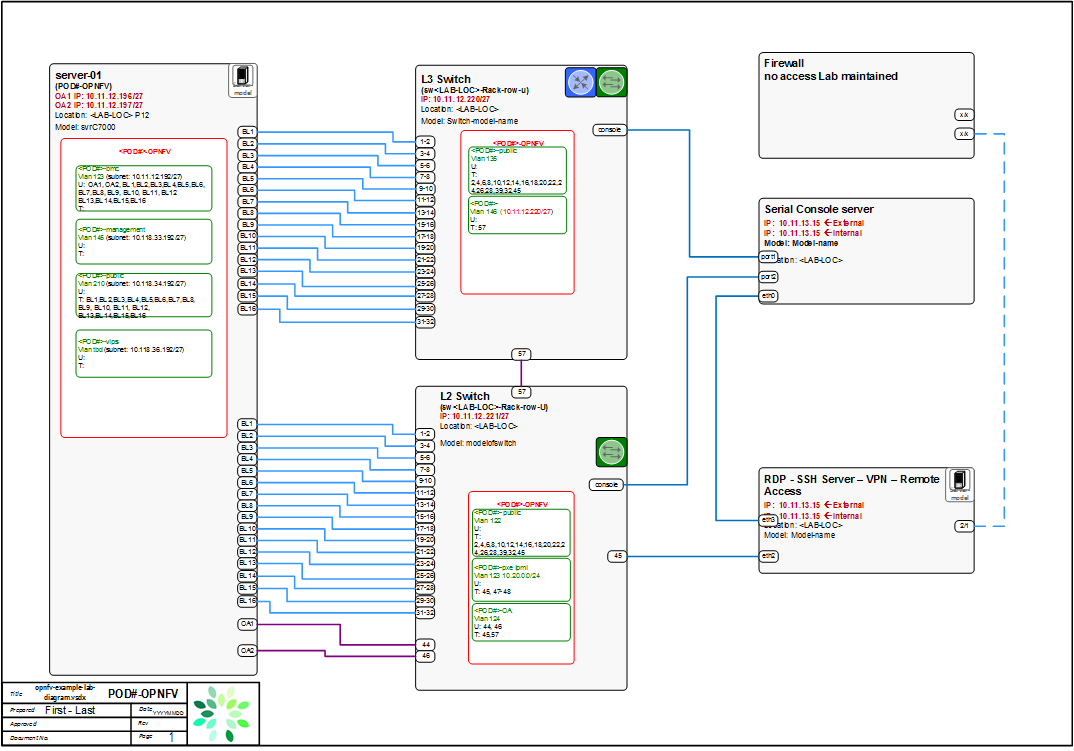
Download the visio zip file here: opnfv-example-lab-diagram.vsdx.zip
2.4. Remote Management¶
Remote access is required for …
- Developers to access deploy/test environments (credentials to be issued per POD / user)
- Connection of each environment to Jenkins master hosted by Linux Foundation for automated deployment and test
OpenVPN is generally used for remote however community hosted labs may vary due to company security rules. For POD access rules / restrictions refer to individual lab documentation as each company may have different access rules and acceptable usage policies.
Basic requirements:
- SSH sessions to be established (initially on the jump server)
- Packages to be installed on a system (tools or applications) by pullig from an external repo.
Firewall rules accomodate:
- SSH sessions
- Jenkins sessions
Lights-out management network requirements:
- Out-of-band management for power on/off/reset and bare-metal provisioning
- Access to server is through a lights-out-management tool and/or a serial console
- Refer to applicable light-out mangement information from server manufacturer, such as ...
Linux Foundation Lab is a UCS-M hardware environment with controlled access as needed
- Access rules and procedure are maintained on the Wiki
- A list of people with access is maintained on the Wiki
- Send access requests to infra-steering@lists.opnfv.org with the following information ...
- Name:
- Company:
- Approved Project:
- Project role:
- Why is access needed:
- How long is access needed (either a specified time period or define “done”):
- What specific POD/machines will be accessed:
- What support is needed from LF admins and LF community support team:
- Once access is approved please follow instructions for setting up VPN access ... https://wiki.opnfv.org/get_started/lflab_hosting
- The people who require VPN access must have a valid PGP key bearing a valid signature from LF
- When issuing OpenVPN credentials, LF will be sending TLS certificates and 2-factor authentication tokens, encrypted to each recipient’s PGP key
3. Pharos Templates and Configuration Files¶
Lab and POD templates are provided to help lab owners document capabilities, configurations and network topologies. Compute, network and storage specifications with network topology details are required to help developers use lab resources efficiently while minimizing support needs. This also greatly assists with troubleshoting. It is the responsibility of the lab owner to keep individual lab documents updated and determine appropriate level of detail that is exposed publicly through the Wiki or maintained in a secure Pharos repo with controlled access.
The goal of the Pharos Project is automation of resource provisioning. This requires machine readable inventory and network configuration files that follow common format.
3.1. Lab Specification Template¶
3.1.1. Introduction¶
Add an summary of what your lab hosts, its focus areas and purpose
3.1.2. Lab Resources¶
| POD Name | Project(s) | Project Lead(s) | Email(s) | POD Role | Status | Notes |
| POD1 | Project Name | John Doe | john@abc.com | CI: stable | Active |
- POD Name: Use consistent naming / numbering to avoid confusion. Hyperlinked to POD description.
- POD Role: CI stable, CI latest, Dev/test, Stand-alone, Virtual, ...
- Status: Assigned, Configuring, Active, Troubleshooting, Available, ...
3.1.3. Acceptable Usage Policy¶
Define lab user policies and expectations
3.1.4. Remote Access Infrastructure¶
Describe lab remote access setup (typically VPN, also link speed, any known restrictions, etc.)
3.1.5. Remote Access Procedure¶
Define lab process for requesting access to the lab (e.g. VPN guide, how to modify BIOS settings, etc.)
3.1.6. Lab Documentation¶
List lab specific documents here
3.1.7. Lab Topology¶
Provide a diagram showing the network topology of lab including lights-out network. Any security sensitive details should not be exposed publically. The following diagram is an example only.
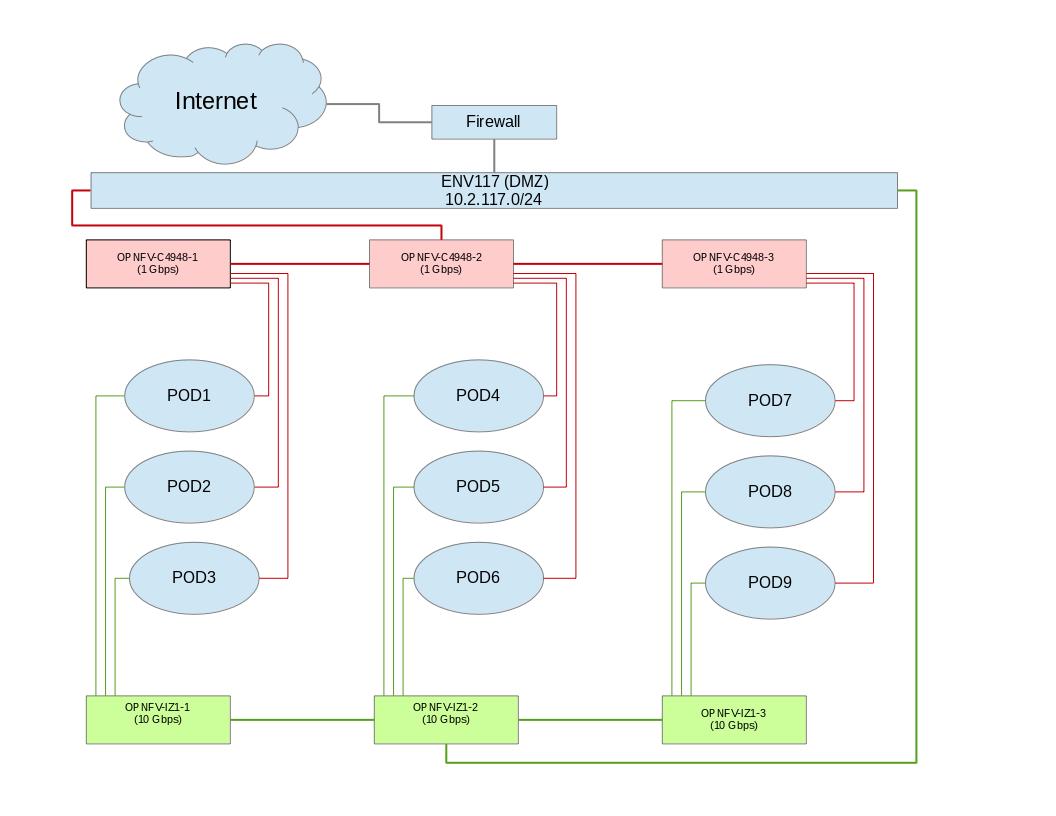
3.2. POD Specification Template¶
3.2.1. Introduction¶
Add an summary of the POD usage (Project, CI stable, CI latest, dev/test, stand-alone servers, etc.)
3.2.2. Additional Requirements¶
Describe any addional POD requirements beyond a standard Pharos compliant POD e.g. test equipment, shared usage, ...
3.2.3. Server Specifications¶
Jump Host
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory | Local Storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| jump | Dell | R730 | ABCDEF007 | E5-2699x2 | 64 GB | 240GB SSD 1 TB SATA | 10.10.10.10 00:1E:67:D4:36:9A root/root | IF0: 10.2.117.36 00:1E:67:4F:B7:B1 VLAN 984 Public IF1: 10.2.1.1 00:1E:67:4F:B7:B2 VLAN 201 Admin | IF2: 10.2.12.1 00:1E:67:4F:B7:B4 VLAN 202 Private IF3: 10.2.13.1 00:1E:67:4F:B7:B5 VLAN 203 Storage |
Compute Nodes
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory | Local Storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| node1 | ||||||||||
| node2 | ||||||||||
| node3 | ||||||||||
| node4 | ||||||||||
| node5 |
3.2.4. VPN Users¶
| Name | Project | Role | Notes | |
| joe user | ju@gmail.com | Pharos | contributer | CI support |
3.2.5. Firewall Rules¶
| Port(s) | Service | Notes |
| 22, 43, 80 | Jenkins CI |
3.2.6. POD Topology¶
Provide a diagram showing the network topology of the POD. Any security sensitive details should not be exposed publically and can be stored in the secure Pharos repo. The following diagram is an example only.
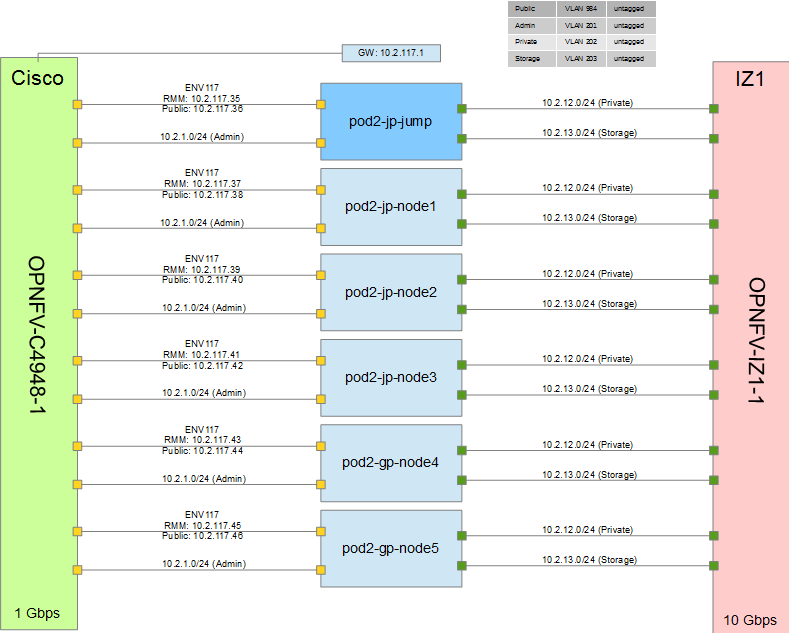
3.3. POD Inventory File¶
The Common Inventory File provides a template for machine reabable input into every installer. For convenience the YAML file template currently resides in the Genesis Project repo. Refer to the following patch for further infomation https://gerrit.opnfv.org/gerrit/#/c/4079.
4. Pharos Configuration¶
OPNFV development, test and production activities rely on Pharos resources and support from the Pharos community. Lab owners and Pharos project committers/contributors will evolve the vision for Pharos as well as expand lab capabilities that are needed to help OPNFV be highly successful.
Pharos configuration documents provide information on how to setup hardware and networks in a Pharos compliant lab. Jira is used to track Pharos activities including lab operations. Lab resources can be used for and declared as either Development (bare-metal or virtual) or Production/CI (bare-metal or virtual). If a resource is used for and declared as Development resource, it can not be used for and declared as Production/CI resource at the same time and vice versa. Changing the resource declation must be brought in to Infra WG. Production/CI PODs are required to be connected to OPNFV Jenkins and available on a 24/7 basis other than scheduled maintenance and troubleshooting. Jenkins slave status can be seen on Jenkins dashboard https://build.opnfv.org/ci/computer/.
4.1. Lab Setup Guide¶
Provides an overview for setting up a Pharos lab. A full set of PHAROS documents are maintained in the pharos repo.
When setting up an OPNFV community lab ...
- Provide the Pharos community with details of the intended setup, including ...
- Overview of resources are being offered to the community, intended purpose and known limitations
- Lab owner name with contacts
- Timelines for availablity for development, test, release production, ...
- Update the Pharos Wiki with lab details
- Lab map, organization, contacts, status, location, resources, role, etc.
- Community labs
- Updating Pharos Documents
- Update the Pharos project information file “Current Labs”
- pharos_information
- Create new Wiki pages for lab and POD specific information
- Access procedures
- Usage guidelines for developers
- Update infomtation as PODs are re-assigned or usage/availability changes
- Fill Lab and POD templates ... ZTE SH Lab Specification ... ZTE SH POD3 Specification
- Note that security sensitive lab information should be stored in the secure Pharos repo
- Connect PODs to Jenkins/CI
4.2. Updating Pharos Documents¶
Details about each Community Lab is found in 3 places:
Summary of lab including location, contacts, status, etc. on the Pharos Project Wiki page
Lab specific details are provided with dedicated Wiki pages, see this Example Lab
Pharos repo docs ...
- docs/information/pharos.rst ... project information file
- docs/labs/ ... Lab documents (includes lab specific capabilities, usages and policies; POD information)
- docs/labs/images/ ... Lab and POD toplogies
4.2.1. Update Pharos repo¶
Clone the Pharos Git repository
- Make the changes to Pharos project information file (docs/information/pharos.rst)
- After code gets merged http://artifacts.opnfv.org/pharos/docs/information/pharos.html will contain your change
4.2.2. Update Pharos Wiki¶
Edit Wiki page
- https://wiki.opnfv.org/pharos
- Look for {{scrape>http://artifacts.opnfv.org/pharos/docs/information/pharos.html}}
- Click “Preview” and see if your change is shown; if shown add a short “Edit summary” and click “Save” (Wiki does not auto update content)
You will see a section of code as shown below. Add your page to the bullet list with wiki link, nice name, and location summary
Update the map info on the Pharos Project Page https://wiki.opnfv.org/pharos?&#community_labs
You will see a section of code as shown below. Add your lab infomation to the list with a comma separated list as follows:
- longitude
- latitude
- .8 <- for size
- marker color png ([[marker-green.png|marker-green.png]], [[marker-blue.png|marker-blue.png]], [[marker-red.png|marker-red.png]], [[marker-gold.png|marker-gold.png]])
- Nice Format Lab Name
- ‘’;’‘
- Location Summary
- ‘’\’’ <– for a new line
- external link: <– optional
MAP:
<olmap id="olMapOne" width="877px" height="200px" lat="45.0" lon="0.0" zoom="3" statusbar="1" toolbar="1" controls="1"
poihoverstyle="0" baselyr="OpenStreetMap" gpxfile="" kmlfile="">
45.52,-122.67,60,.8,marker-red.png,Linux Foundation;Portland, Oregon \\ external link: [[http://www.test.com|test.com]]
39.7392,-104.9902,60,.8,marker-red.png,Cable Labs;Denver, CA \\ external link: [[http://www.test.com|test.com]]
37.333685,-121.891272,60,.6,marker-green.png,[[pharos/spirentvctlab|Spirent VCT Lab]] \\ San Jose, California
39.90,116.35,60,.8,marker-red.png,China Mobile Labs;Beijing, China \\ external link: [[http://www.test.com|test.com]]
37.413137,-121.977975,-180,.6,marker-red.png,Dell Labs;Santa Clara, California \\ link: [[https://wiki.opnfv.org/dell_hosting]]
59.41,17.95,60,.8,marker-red.png,Enea Pharos Lab;Kista, Sweden \\ external link: [[http://www.enea.com/pharos-lab|ENEA pharos lab]]
45.50,-73.66,60,.8,marker-blue.png,Ericsson Labs;Montreal, Canada \\ external link: [[http://www.test.com|test.com]]
34.26,108.97,60,.8,marker-green.png, Huawei Labs;Xi an, China \\ external link: [[http://www.test.com|test.com]]
37.373424,-121.964913,60,.8,marker-green.png, Huawei Labs;Santa Clara, USA \\ external link: [[http://www.test.com|test.com]]
45.53,-122.97,60,.8,marker-green.png,Intel Labs;Hillsboro, Oregon \\ link: [[https://wiki.opnfv.org/get_started/intel_hosting|intel_hosting]]
48.75867,-3.45196,60,.8,marker-gold.png,Orange Labs;Lannion, France \\ external link: [[http://www.test.com|test.com]]
48.825786,2.274797,-60,.8,marker-gold.png,Orange Labs;Paris, France \\ external link: [[http://www.test.com|test.com]]
31.97,118.79,60,.8,marker-red.png,ZTE Labs;Nan Jing, China \\ link:[[zte-nj-testlab|ZTE, Nan Jing]]
[[http://test.com|test.com]] \\ internal link: [[::start]]\\ **DW Formatting**
</olmap>
4.3. Jump Server Configuration¶
Jump server install procedures are maintained by each installer project. Addional Jump server configuraton BKMs will be maintained here. The below install information was used for Fuel however may be outdated (please refer to Fuel Installer documents).
Procedure
- Obtain CentOS 7 Minimal ISO and install
wget http://mirrors.kernel.org/centos/7/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-Minimal-1503-01.iso
- Set parameters appropriate for your environment during installation
- Disable NetworkManager
systemctl disable NetworkManager
- Configure your /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-* files for your network
- Restart networking
service network restart
- Edit /etc/resolv.conf and add a nameserver, for example 8.8.8.8
echo nameserver 8.8.8.8 >> /etc/resolv.conf
- Install libvirt & kvm
yum -y updateyum -y install kvm qemu-kvm libvirtsystemctl enable libvirtd
- Reboot:
shutdown -r now
- Configure SSHD
If you wish to avoid annoying delay when use ssh to log in, disable DNS lookups:
When UseDNS is existed in the config file, update it:
sed -i -e 's/^#*UseDNS\ \+yes/UseDNS no/' /etc/ssh/sshd_configor append the setting when not existed:
echo UseDNS no >> /etc/ssh/ssd_configDisable Password Authenticaion for security:
sed -i -e 's/^#PasswordAuthentication\ \+yes/PasswordAuthentication no/' /etc/ssh/sshd_configIf you want to disable IPv6 connections, comment IPv6 ListenAddress and change AddressFamily to inet:
sed -i -e 's/^ListenAddress\ \+::/#ListenAddress ::/' /etc/ssh/sshd_configsed -i -e 's/^AddressFamily\ \+any/AddressFamily inet/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- Restart sshd
systemctl restart sshd
- Install virt-install
yum -y install virt-install
- Visit artifacts.opnfv.org and D/L the OPNFV Fuel ISO
- Create a bridge using the interface on the PXE network, for example: br0
brctl addbr br0
- Make a directory owned by qemu:
mkdir /home/qemu; mkdir -p /home/qemu/VMs/fuel-6.0/disk
chown -R qemu:qemu /home/qemu
- Copy the ISO to /home/qemu
cd /home/qemu
virt-install -n opnfv-2015-05-22_18-34-07-fuel -r 4096 --vcpus=4 --cpuset=0-3 -c opnfv-2015-05-22_18-34-07.iso --os-type=linux --os-variant=rhel6 --boot hd,cdrom --disk path=/home/qemu/VMs/mirantis-fuel-6.0/disk/fuel-vhd0.qcow2,bus=virtio,size=50,format=qcow2 -w bridge=br0,model=virtio --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0
- Temporarily flush the firewall rules to make things easier:
iptables -F
- Connect to the console of the installing VM with your favorite VNC client.
- Change the IP settings to match the pod, use an IP in the PXE/Admin network for the Fuel Master
5. PHAROS Community Labs¶
5.1. Dell OPNFV Testlab¶
5.1.1. Overview¶
Dell is hosting an OPNFV testlab at its Santa Clara facility. The testlab would host baremetal servers for the use of OPNFV community as part of the OPNFV Pharos Project
- The Dell Testlab consists of 2 PODs
- POD1 for Fuel
- POD2 for Foreman

- Each of the 2 PODs consists of 6 servers that consist of
- 1 Jump Server
- 3 Servers for Control Nodes
- 2 Servers for Compute Nodes
5.1.2. Hardware details¶
All the servers within the two PODs reside within a single Dell PowerEdge 620 chassis and have the following specifications:
POD1-Fuel¶
| Hostname | Model | Memory | Storage | Processor | Socket |
| Fuel Jump Server | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 1200GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node2 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node3 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node4 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node5 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node6 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
POD2-Foreman¶
| Hostname | Model | Memory | Storage | Processor | Socket |
| Foreman Jump Server | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node7 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node8 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node9 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node11 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node12 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
5.1.3. Software¶
The Jump servers in the Testlab are pre-provisioned with the following softwares:
- Fuel-Jump Server:
- OS: Ubuntu 14.04
- Foreman-Jump Server:
- OS: CentOS7
5.1.4. Networks¶
POD1-Fuel¶
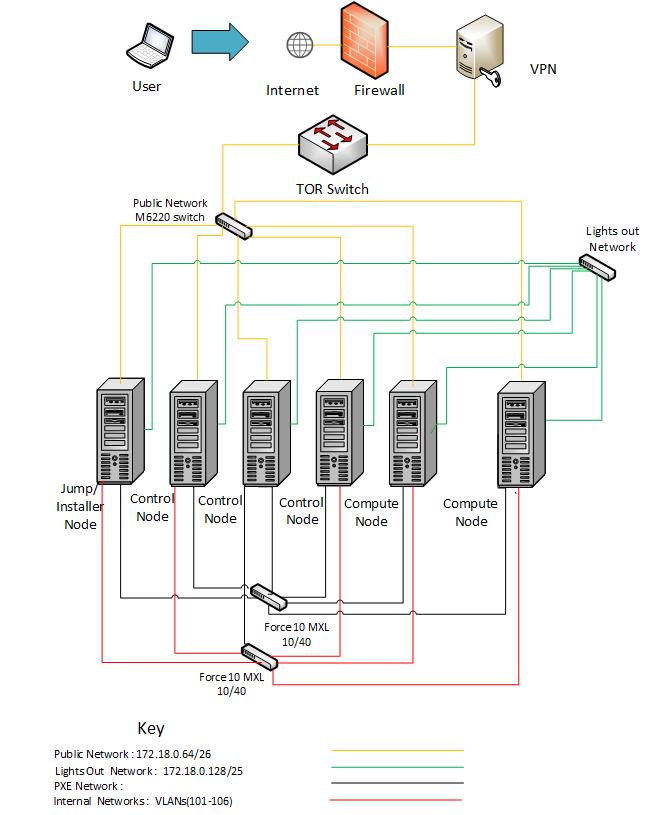
| Hostname | NIC Model | Ports | MAC | BW | Roles |
| Fuel Jump | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:81 | 10G | Unused |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:84 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:85 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:87 | 10G | Fuel Admin/mgmt/pvt/ storage | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:89 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8B | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node2 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8E | 10G | Unused |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:91 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:92 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:94 | 10G | Fuel Admin/mgmt/pvt/ storage | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:96 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:98 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node3 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:9B | 10G | Unused |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:9E | 10G | Unused | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:9F | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A1 | 10G | Fuel Admin/mgmt/pvt/ storage | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A3 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A5 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node4 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A8 | 10G | Unused |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:AB | 10G | Unused | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:AC | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:AE | 10G | Fuel Admin/mgmt/pvt/ storage | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B0 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B1 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node5 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B5 | 10G | Unused |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B8 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B9 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:BB | 10G | Fuel Admin/mgmt/pvt/ storage | ||
| 3, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:BD | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C0 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node6 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C2 | 10G | Unused |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C5 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C6 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C8 | 10G | Fuel Admin/mgmt/pvt/ storage | ||
| 3, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:CA | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:CD | 10G | Unused |
POD2-Foreman¶
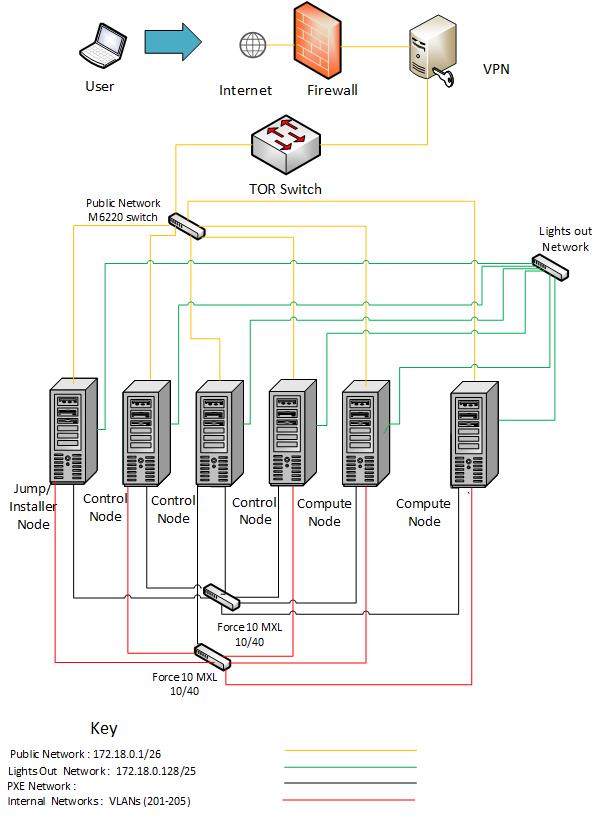
| Hostname | NIC Model | Ports | MAC | BW | Roles |
| Foreman Jump | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:1D | 10G | Foreman Admin |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:20 | 10G | Foreman Private/ Storage | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:21 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:23 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, TBD | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:89 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8B | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node7 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:CF | 10G | Foreman Admin |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:D2 | 10G | Foreman Private/ Storage | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:D3 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:D5 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:D7 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:DA | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node8 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:DC | 10G | Foreman Admin |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:DF | 10G | Foreman Private/ Storage | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E0 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E2 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E4 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E7 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node9 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E9 | 10G | Foreman Admin |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:EC | 10G | Foreman Private/ Storage | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:ED | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:EF | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:F1 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:F3 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node11 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:03 | 10G | Foreman Admin |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:06 | 10G | Foreman Private/ Storage | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:07 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:09 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:0B | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:0D | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node12 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:10 | 10G | Foreman Admin |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:13 | 10G | Foreman Private/ Storage | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:14 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:16 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, TBD | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:89 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8B | 10G | Unused |
Subnet allocations¶
| Network name | Address | Mask | Gateway | VLAN id |
| Fuel Admin | 10.20.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | 10.20.0.1 | Untagged |
| Fuel Mangement | 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.0.1 | 101 |
| Fuel Storage | 192.168.1.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 | 102 |
| Fuel Public | 172.18.0.64 | 255.255.255.192 | 172.18.0.65 | Untagged |
| Foreman Admin | 10.4.14.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.4.14.100 | Untagged |
| Foreman Private | 10.4.5.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.4.5.1 | Untagged |
| Foreman Public | 172.18.0.0 | 255.255.255.192 | 172.18.0.1 | Untagged |
| Lights Out | 172.18.0.128 | 255.255.255.128 | 172.18.0.129 | Untagged |
Lights out Network¶
POD1
| Hostname | Lights-out address | MAC | Username | Password |
| Fuel-Jump | 172.18.1.131 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:80 | root | calvin |
| Node2 | 172.18.1.132 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8D | root | calvin |
| Node3 | 172.18.1.133 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:9A | root | calvin |
| Node4 | 172.18.1.134 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A7 | root | calvin |
| Node5 | 172.18.1.135 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B4 | root | calvin |
| Node6 | 172.18.1.136 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C1 | root | calvin |
POD2
| Hostname | Lights-out address | MAC | Username | Password |
| Foreman-Jump | 172.18.1.143 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:1C | root | calvin |
| Node7 | 172.18.1.137 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:CE | root | calvin |
| Node8 | 172.18.1.138 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:DB | root | calvin |
| Node9 | 172.18.1.139 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E8 | root | calvin |
| Node11 | 172.18.1.141 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:02 | root | calvin |
| Node12 | 172.18.1.142 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:0F | root | calvin |
5.1.5. Remote access infrastructure¶
The Dell OPNFV testlab is free to use for the OPNFV community.
A VPN is used to provide access to the Dell Testlab.
- To access the Testlab, please contact Waqas_Riaz@DELL.com with the following details:
- Name
- Designation
- Organization
- Purpose of using the lab
Processing the request can take 2-3 business days.
5.1.7. Overview¶
Dell is hosting an OPNFV testlab at its Santa Clara facility. The testlab would host baremetal servers for the use of OPNFV community as part of the OPNFV Pharos Project
- The Dell Testlab consists of 3 PODs for the use of the community
- POD1 (Jenkins slave: dell-us-testing-bm-1)
- POD2 (Jenkins slave: dell-us-deploying-bm2)
- POD3 (Jenkins slave: dell-us-delpoyingbm3)

- Each of the 2 PODs consists of 6 servers that consist of
- 1 Jump Server
- 3 Servers for Control Nodes
- 2 Servers for Compute Nodes
5.1.8. Hardware details¶
For POD1 and POD2, the servers reside within a single Dell PowerEdge 620 chassis and have the following specifications:
POD1
| Hostname | Model | Memory | Storage | Processor | Socket |
| Jump Server | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 1200GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node2 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node3 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node4 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node5 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node6 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 600GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
POD2
| Hostname | Model | Memory | Storage | Processor | Socket |
| Jump Server | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2630 | 2 |
| Node7 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node8 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node9 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node11 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
| Node12 | Dell PowerEdge M620 | 64 GB | 300GB HDD | Intel Xeon E5-2640 | 2 |
POD3 consists of 6 R630 Rack servers with the following specifications:
POD3
| Hostname | Model | Memory | Storage | Processor | Socket |
| Jump Server | Dell PowerEdge R630 | 128 GB | 750GB SSD | Intel Xeon E5-2698 | 2 |
| Node2 | Dell PowerEdge R630 | 128 GB | 750GB SSD | Intel Xeon E5-2698 | 2 |
| Node3 | Dell PowerEdge R630 | 128 GB | 750GB SSD | Intel Xeon E5-2698 | 2 |
| Node4 | Dell PowerEdge R630 | 128 GB | 750GB SSD | Intel Xeon E5-2698 | 2 |
| Node5 | Dell PowerEdge R630 | 128 GB | 750GB SSD | Intel Xeon E5-2698 | 2 |
| Node6 | Dell PowerEdge R630 | 128 GB | 750GB SSD | Intel Xeon E5-2698 | 2 |
5.1.9. Software¶
The Jump servers in the Testlab are pre-provisioned with the following softwares:
- POD1-Jump Server:
- OS: Ubuntu 14.04
- POD2-Jump Server:
- OS: CentOS7.1
- POD3-Jump Server:
- OS: CentOS7.1
5.1.10. Networks¶
POD1

| Hostname | NIC Model | Ports | MAC | BW | VLANs/Roles |
| Jump Server | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:81 | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:84 | 10G | Internal Networks (101-106) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:85 | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:87 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:89 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8B | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node2 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8E | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:91 | 10G | Internal Networks (101-106) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:92 | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:94 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:96 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:98 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node3 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:9B | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:9E | 10G | Internal Networks (101-106) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:9F | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A1 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A3 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A5 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node4 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A8 | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:AB | 10G | Internal Networks (101-106) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:AC | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:AE | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B0 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B1 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node5 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B5 | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B8 | 10G | Internal Networks (101-106) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B9 | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:BB | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:BD | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C0 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node6 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C2 | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C5 | 10G | Internal Networks (101-106) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C6 | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C8 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:CA | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:CD | 10G | Unused |
POD2

| Hostname | NIC Model | Ports | MAC | BW | Roles |
| Foreman Jump | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:1D | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:20 | 10G | Internal Networks (201-205) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:21 | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:23 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, TBD | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:89 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8B | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node7 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:CF | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:D2 | 10G | Internal Networks (201-205) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:D3 | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:D5 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:D7 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:DA | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node8 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:DC | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:DF | 10G | Internal Networks (201-205) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E0 | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E2 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E4 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E7 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node9 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E9 | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:EC | 10G | Internal Networks (201-205) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:ED | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:EF | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:F1 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:F3 | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node11 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:03 | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:06 | 10G | Internal Networks (201-205) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:07 | 10G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:09 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, Intel 82599 | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:0B | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:0D | 10G | Unused | ||
| Node12 | 1, Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM57810 | em1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:10 | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:13 | 10G | Internal Networks (201-205) | ||
| 2, Intel 82599 | p3p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:14 | 1G | Public | |
| p3p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:16 | 10G | Unused | ||
| 3, TBD | p1p1 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:89 | 10G | Unused | |
| p1p2 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8B | 10G | Unused |
POD3
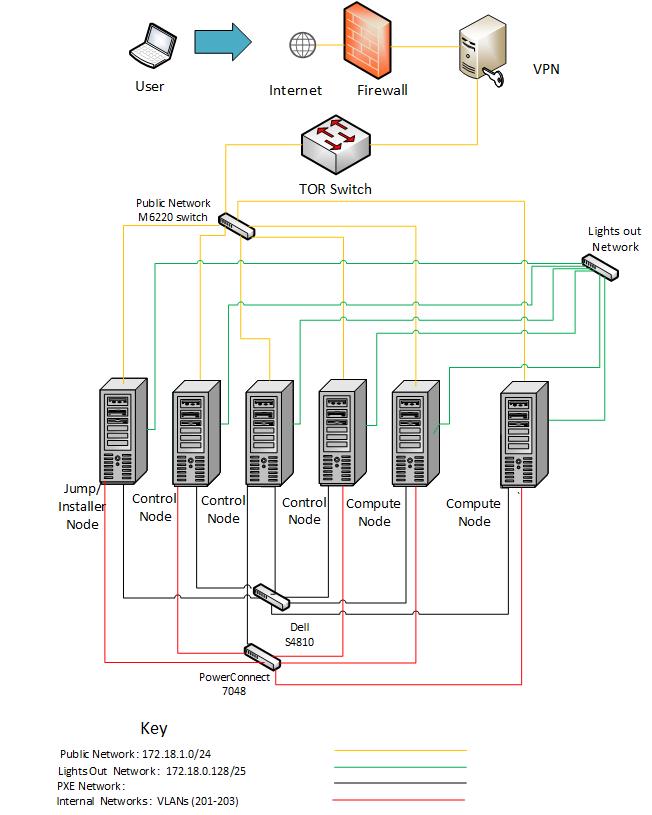
| Hostname | NIC Model | Ports | MAC | BW | Roles (VLANs) |
| Jump Server | 1, Intel 2P X520/2P I350 rNDC | em1 | EC:F4:BB:D7:14:20 | 1G | PXE |
| em2 | EC:F4:BB:D7:14:22 | 10G | Internal Networks (201,202,203) | ||
| p3p1 | EC:F4:BB:D7:14:24 | 1G | Public | ||
| Node1 | 1, Intel 2P X520/2P I350 rNDC | em1 | EC:F4:BB:D6:F2:98 | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | EC:F4:BB:D6:F2:9A | 10G | Internal Networks (201,202,203) | ||
| p3p1 | EC:F4:BB:D6:F2:9C | 1G | Public | ||
| Node2 | 1, Intel 2P X520/2P I350 rNDC | em1 | EC:F4:BB:D6:F9:10 | 1G | PXE |
| em2 | EC:F4:BB:D6:F9:12 | 10G | Internal Networks (201,202,203) | ||
| p3p1 | EC:F4:BB:D6:F9:14 | 1G | Public | ||
| Node3 | 1, Intel 2P X520/2P I350 rNDC | em1 | EC:F4:BB:D7:C9:B8 | 1G | PXE |
| em2 | EC:F4:BB:D7:C9:BA | 10G | Internal Networks (201,202,203) | ||
| p3p1 | EC:F4:BB:D7:C9:BC | 1G | Public | ||
| Node4 | 1, Intel 2P X520/2P I350 rNDC | em1 | EC:F4:BB:D7:16:E8 | 10G | PXE |
| em2 | EC:F4:BB:D7:16:EA | 10G | Internal Networks (201,202,203) | ||
| p3p1 | EC:F4:BB:D7:16:EA | 1G | Public | ||
| Node5 | 1, Intel 2P X520/2P I350 rNDC | em1 | EC:F4:BB:D6:FE:98 | 1G | Unused |
| em2 | EC:F4:BB:D6:FE:9A | 10G | Internal Networks (201,202,203) | ||
| p3p1 | EC:F4:BB:D6:FE:9C | 1G | Public |
Subnet allocations
| Network name | Address | Mask | Gateway | VLAN id |
| POD1 Public | 172.18.0.64 | 255.255.255.192 | 172.18.0.65 | Untagged |
| POD2 Public | 172.18.0.0 | 255.255.255.192 | 172.18.0.1 | Untagged |
| POD3 Public | 172.18.1.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.18.1.1 | Untagged |
| Lights Out | 172.18.0.128 | 255.255.255.128 | 172.18.0.129 | Untagged |
Lights out Network
POD1
| Hostname | Lights-out address | MAC | Username | Password |
| Jump | 172.18.0.131 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:80 | root | calvin |
| Node2 | 172.18.0.132 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:8D | root | calvin |
| Node3 | 172.18.0.133 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:9A | root | calvin |
| Node4 | 172.18.0.134 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:A7 | root | calvin |
| Node5 | 172.18.0.135 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:B4 | root | calvin |
| Node6 | 172.18.0.136 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:C1 | root | calvin |
POD2
| Hostname | Lights-out address | MAC | Username | Password |
| Jump | 172.18.0.143 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:1C | root | calvin |
| Node7 | 172.18.0.137 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:CE | root | calvin |
| Node8 | 172.18.0.138 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:DB | root | calvin |
| Node9 | 172.18.0.139 | A4:1F:72:11:B4:E8 | root | calvin |
| Node11 | 172.18.0.141 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:02 | root | calvin |
| Node12 | 172.18.0.142 | A4:1F:72:11:B5:0F | root | calvin |
POD3
| Hostname | Lights-out address | MAC | Username | Password |
| Jump | 172.18.0.181 | 74:E6:E2:FA:BB:D8 | root | calvin |
| Node1 | 172.18.0.182 | 74:E6:E2:FA:E9:2E | root | calvin |
| Node2 | 172.18.0.183 | 74:E6:E2:FA:FC:E2 | root | calvin |
| Node3 | 172.18.0.184 | 74:E6:E2:FB:05:68 | root | calvin |
| Node4 | 172.18.0.185 | 74:E6:E2:FA:A4:02 | root | calvin |
| Node5 | 172.18.0.186 | 74:E6:E2:FA:E4:18 | root | calvin |
5.1.11. Remote access infrastructure¶
The Dell OPNFV testlab is free to use for the OPNFV community.
A VPN is used to provide access to the Dell Testlab.
To access the Testlab, please visit the Dell OPNFV Lab’s wiki page (https://wiki.opnfv.org/dell_hosting) for details.
5.1.12. Accessing the Teslab¶
POD1 JumpServer
IP: 172.18.0.67
User: opnfv
Passwd: d3ll1234
POD2 JumpServer
IP: 172.18.0.11
User: opnfv
Passwd: d3ll1234
POD3 JumpServer
IP: 172.18.1.3
User: opnfv
Passwd: d3ll1234
5.2. ERICSSON OPNFV Lab Configuration Files¶
5.2.1. Ericssion OPNFV Lab Specification¶
Introduction¶
Ericsson OPNFV Lab currently has 2 Bare Metal and 3 Virtual PODs available globally (hosted in the GIC). Each POD has 5 servers, comprised of 3 controller nodes (HA) and 2 computes nodes. NOTE: (this make differ depending on scenario).
These PODs are dedicated for use by Production/CI. These PODs focus on providing verification, build, deploy and testing for scenarios related with test projects, installer projects and perforamnce enhancement projects, such as KVM, OVS, FDS, etc.
In addition to the full-time CI/CD resources, the Ericsson OPNFV lab provides developer labs (DRs) for project usage, testing and development.
Scenarios services by this lab are:
Scenario defitions can be found here: Colorado Scenario Status
Lab Resources¶
| POD Name | Project(s) | PTL(s) | Email(s) | POD Role | Status | Notes |
| POD1 | CI/CD | Daniel Smith | daniel.smith@ericsson.com | CI: latest | Active | BM-CI |
| POD2 | CI/CD | Daniel Smith | daniel.smith@ericsson.com | CI: latest | Active | BM-CI |
| vPOD1 | CI/CD | Fatih Degirmenci | fatih.degirmenci@ericsson.com | CI: latest | Active | Virt-CI |
| PHAROS-166 | FUEL | Constant Wette | constant.wette@ericsson.com | DR: B-rel | Active | Nested |
| PHAROS-167 | OVSNFV | Billy O’Mahoney | billy.omahoney@intel.com | DR: C-rel | Active | Hybrid |
| PHAROS-174 | GLUON | Bin Hu | bh526r@att.com | DR: D-rel | Active | Nested* |
| PHAROS-180 | SAVI |
|
richard.brunner@ericsson.com | DR: D-rel | Active | Nested* |
| PHAROS-181 | IPV6-MULTI |
|
bh526r@att.com | DR: D-rel | Active | Nested* |
| PHAROS-191 | AUTO-DEP |
|
Peter.Barabas@ericsson.com | DR: C-rel | Active | Nested* |
| PHAROS-199 | SDN-L3 |
|
Tim.Irnich@ericsson.com | DR: C-rel | Active | Nested* |
| PHAROS-236 | LLT-TOOL |
|
Jose.Lausuch@ericsson.com | DR: C-rel | Active | Nested* |
| PHAROS-253 | ODL-II |
|
Nikolas.Hermanns@ericsson.com | DR: C-rel | Active | Nested* |
Acceptable Usage Policy¶
Resources located in Ericsson OPNFV lab shall only be used for CI, infra setup/configuration and troubleshooting purposes. No development work is allowed in these PODs. Development Work should only be performed on the DR labs assigned to individual projects.
Remote Access Infrastructure¶
Ericsson OPNFV lab provides a SSH GW that allows for unlimited port-forwarding, as well as Remote Desktop, VNC and SOCKS proxy capability allowing the end user to feel as though directly connected to the lab.
Remote Access Procedure¶
Access to this environment can be granted by sending an e-mail to: daniel.smith@ericsson.com.
Subject: ericsson opnfv access.
The following information should be provided in the request:
Full name:
E-mail:
Organization:
Why is access needed:
How long is access needed:
Number of Hosts required:
Topology Required (HA, SA):
Feature/Plugins/Options Required (DPDK, ODL, ONOS):
Enclosed a copy of your id_rsa.pub (public key) with your request and a login will be created for you
Lab Documentation¶
Lab Topology¶

Each POD is an individual entity with its own set of independant networks allowing for interconnection between DR labs, intra connectinos within multiple Nested DRs all without touching the CI/CD running in production.
Refer to each Lab specific wiki page for IP and Login and Topology Information.
5.3. Huawei’s OPNFV Lab¶
5.3.1. Huawei’s Lab Specification¶
Introduction¶
Huawei’s lab providing 5 PODs for baremetal deployment, 4 standalone servers for virtual deployment. All the resources have been attached to jenkins master, you can view the slaves below in jenkins master. Current POD assignments and individual POD details are listed below.
| Resource | Project(s) | POD Role | Status |
| huawei-pod1 | compass4nfv | CI Stable | Active |
| huawei-pod2 | compass4nfv | CI Stable | Active |
| huawei-pod3 | yardstick | Dev/Test | Active |
| huawei-pod4 | compass4nfv | CI Stable | Active |
| huawei-pod5 | compass4nfv | CI Stable | Active |
| huawei-virtual1 | compass4nfv | CI Stable | Active |
| huawei-virtual2 | compass4nfv | CI Stable | Active |
| huawei-virtual3 | compass4nfv | CI Stable | Active |
| huawei-virtual4 | compass4nfv | CI Stable | Active |
Acceptable Usage Policy¶
All of these resources above are used for OPNFV CI, if there is any requirement by OPNFV contributor or committer for the purpose of OPNFV development, please apply to us for permission.
Remote Access Infrastructure¶
Huawei provides VPN(OpenVPN) to connect the lab.
Remote Access Procedure¶
This environment is free to use by any OPNFV contributor or committer for the purpose of OPNFV approved activities, you just need to obtain VPN credentials to access.
- Access to this environment can be granted by sending a e-mail to:
Following information should be provided in the request:
- subject: opnfv_huawei_access
- Full name
- Phone
- Organization
- OPNFV Contributor/Committer name :
- OPNFV Project(s) Association:
- LF ID:
- Recommended by:
- PGP public key (preferably registered with a PGP PKI server)
- SSH public key
Granting access normally takes 3-5 business days.
Detailed access descriptions will be provided with your access grant e-mail.
Lab Documentation¶
Lab Topology¶
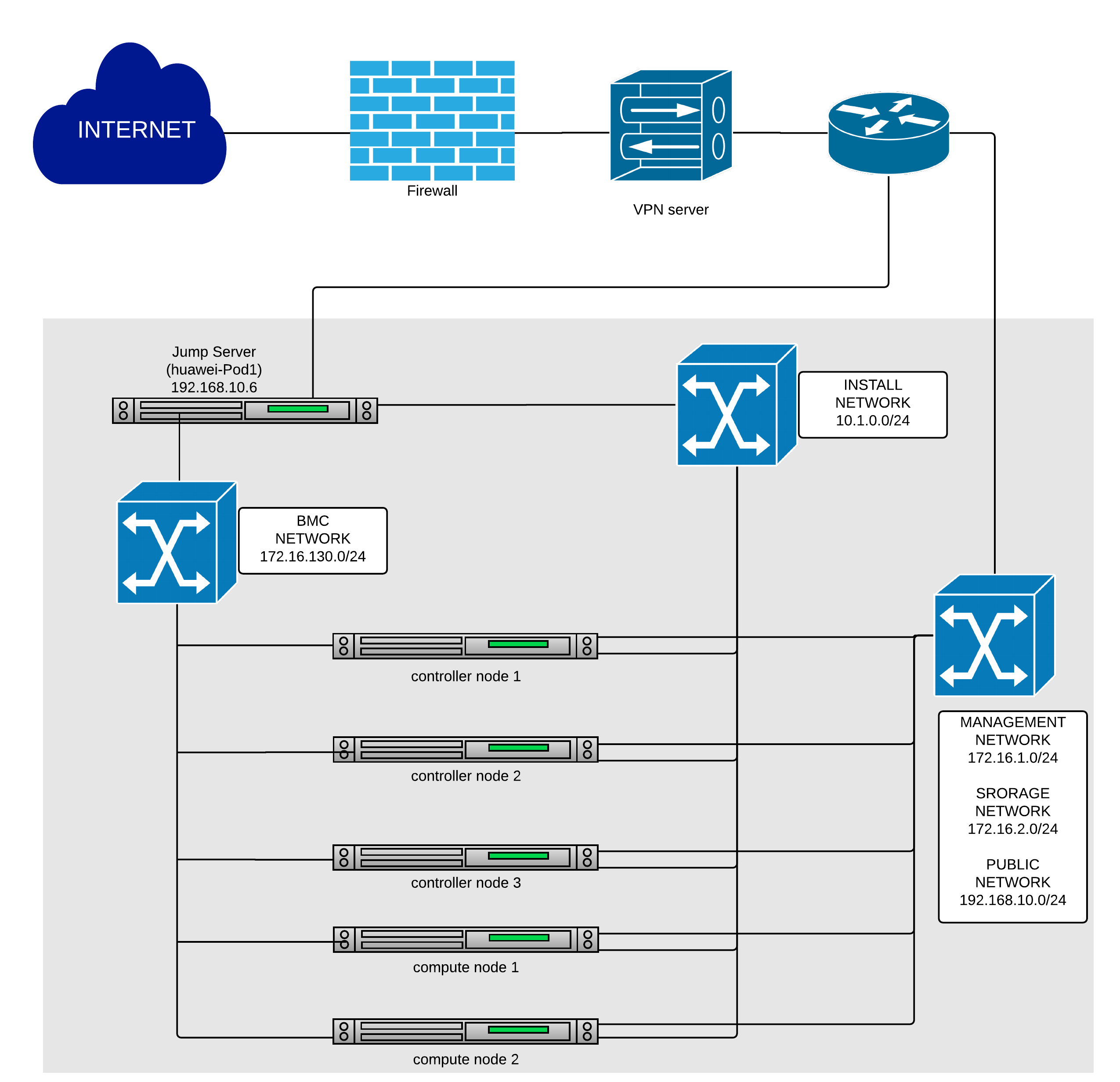
Below you’ll find a topological view of the hosting set-up,you can get more detailed information from the individual POD.

Figure 1: Huawei lab OPNFV hosting environment overview
5.3.2. Huawei PODs Specification¶
NOTE: Illustrated by the example of huawei-pod1&huawei-virtual1.
huawei-pod1¶
This is a bare metal deployment pod deployed by compass installer
- the pod1 consist of 6 Rack servers, the following is detail
| Hostname | CPU | Storage | Memory | ipmi Mac &ip |
| jumpserver | Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU X5650 @ 2.67GHz | 1.8TB | 31G | |
| Host1 controller | Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2690 @ 2.90GHz | 4.2TB | 188G | eth3:Mac F8:4A:BF:55:A2:8E ip 172.16.130.26 |
| Host2 controller | Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2670@ 2.60GHz | 6TB | 188G | eth3:Mac D8:49:0B:DA:5A:B8 ip 172.16.130.27 |
| Host3 controller | Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2670@ 2.60GHz | 8.4TB | 188G | eth3:Mac 78:D7:52:A0:B1:9D ip 172.16.130.29 |
| Host4 compute | Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2670@ 2.60GHz | 7.2TB | 188G | eth3:Mac D8:49:0B:DA:5B:5E ip 172.16.130.30 |
| Host5 compute | Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2670@ 2.60GHz | 4.8TB | 188G | eth3:Mac D8:49:0B:DA:56:86 ip 172.16.130.31 |
- 1 Huawei S9300 10G switch for storage, management and public traffic - 2x10GE to each server.
- 1 Huawei S5300 1G switch for installing and Lights+out management traffic - 2x1GE to each server.
- 1 VPN concentrator for remote access and management.
- 1 Huawei firewall and router for public network secure access.
Below you’ll find a topological view of the huawei-Pod1 set-up:
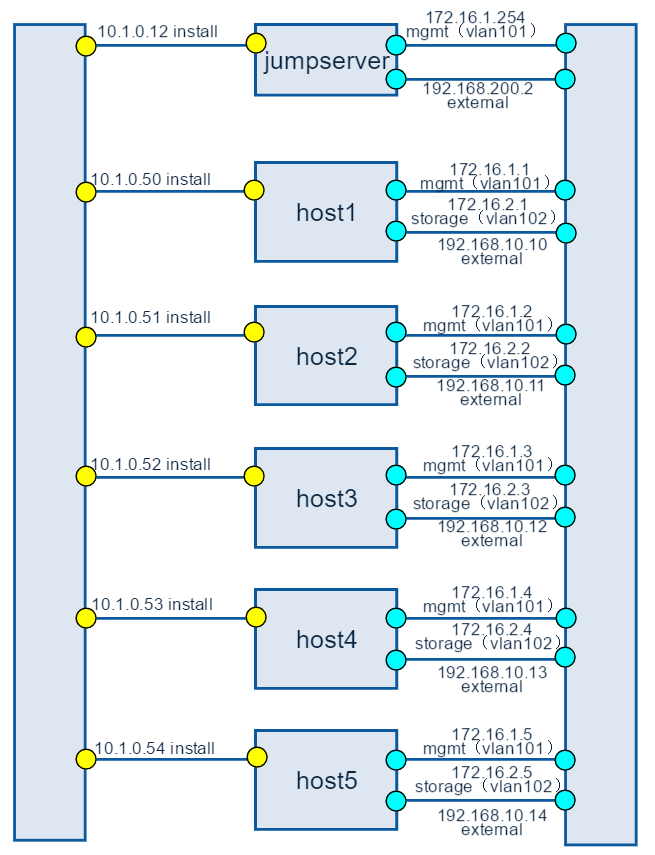
Figure 2: Full Pod network configuration
huawei-virtual1¶
This is a virtual deployment POD deployed by compass installer
virtual pod consist of one standalone server
| name | huawei-virtual1 |
| CPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2680 v3 @ 2.50GHz |
| Memory | 251G |
| Storage | 4TB |
| IP | 192.168.107.2 |
Below you’ll find a topological view of the huawei-virtual1 Pod set-up:
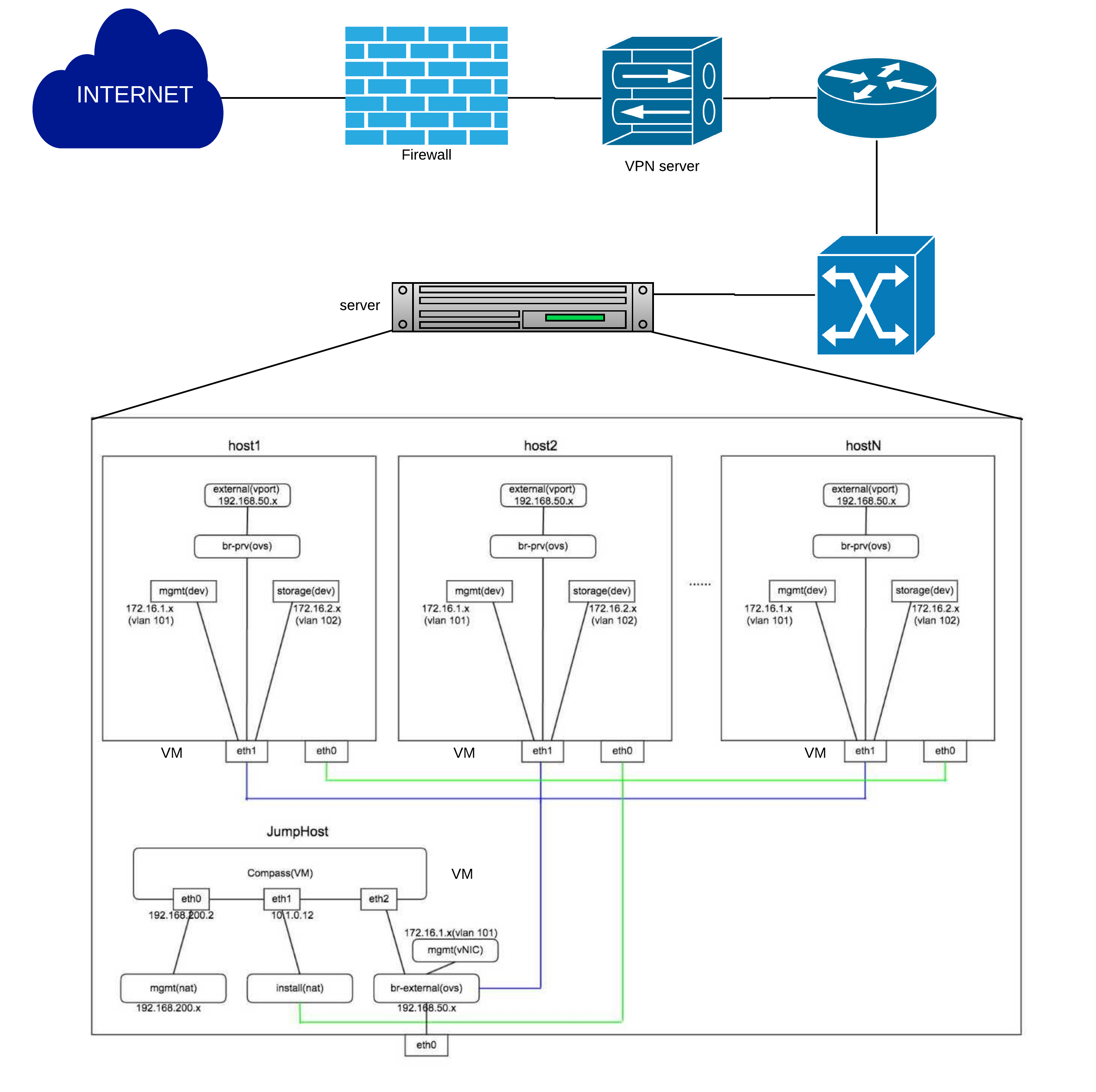
Figure 3: virtual deployment pod network configuration
5.4. OOL OPNFV Testbed¶
5.4.1. Lab: OOL OPNFV Testbed¶
Introduction¶
Okinawa Open Laboratory (OOL) provides the following facilities for OPNFV testing. The testlab is now located only at Okinwa in Japan.
Lab Resources¶
| POD Name | Project(s) | Project Lead(s) | Email(s) | POD Role | Status | Notes |
| ool-pod1 | CI stable | Available | ||||
| ool-virtual1 | Doctor | Ryota Mibu | r-mibu@cq.jp.nec.com | CI review | Assigned |
Acceptable Usage Policy¶
These resources provided to OPNFV are free to use by any OPNFV contributor or committer for the purpose of OPNFV approved activities by permission of the operator, but shall be used for CI, infra setup/configuration and troubleshooting purposes.
Remote Access Infrastructure¶
OOL provide VPN(OpenVPN) to connect this testlab.
Remote Access Procedure¶
Access to this environment can be granted by sending a e-mail to: TBD
subject: opnfv_access_ool
Following information should be provided in the request:
- Full name
- Phone
- Organization
- Resources required
- How long is access needed
- PGP public key
- SSH public key
Granting access normally takes 2-3 business days.
Detailed access descriptions will be provided with your access grant e-mail.
Lab Documentation¶
Lab Topology¶
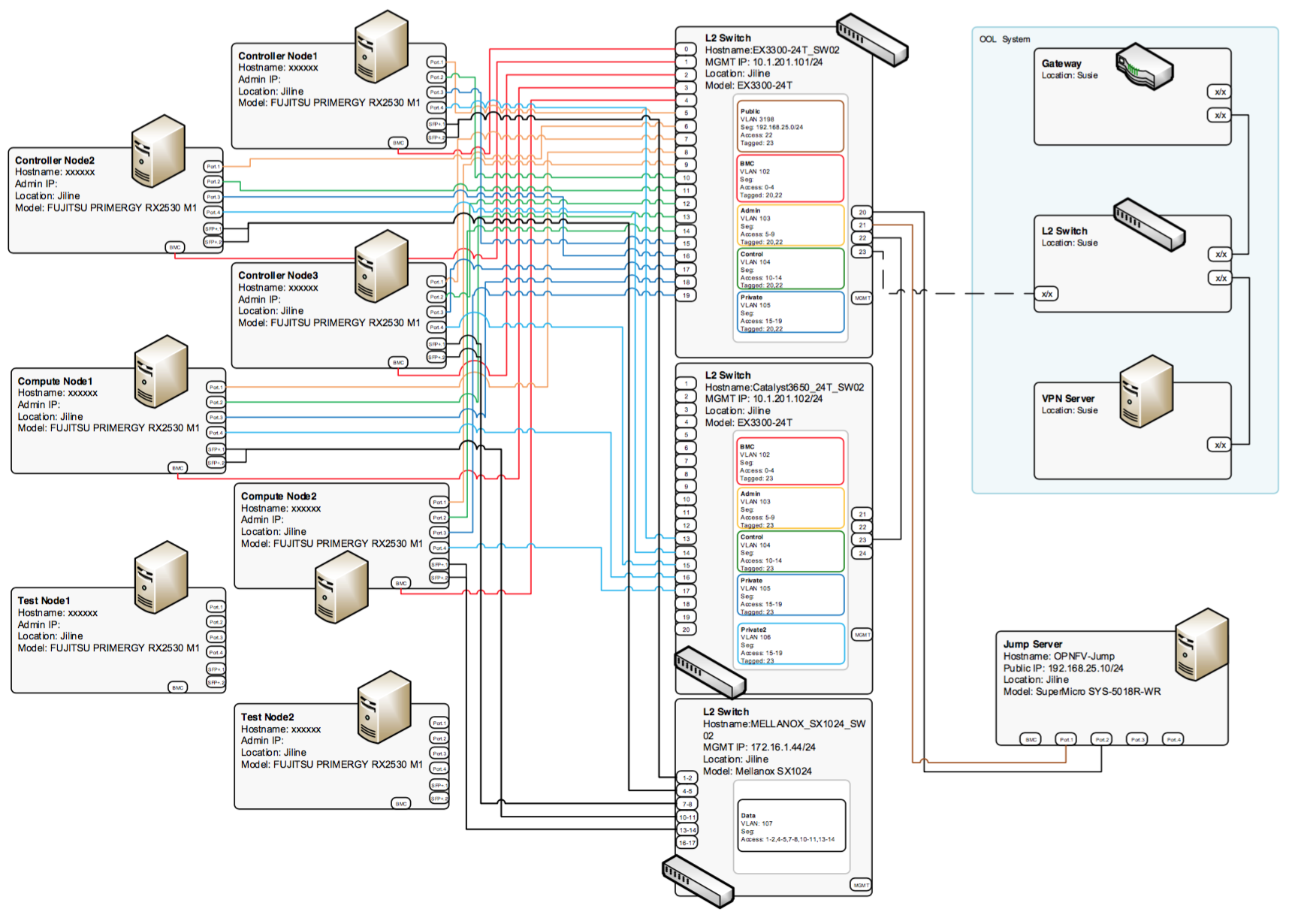
5.4.2. POD: ool-pod1¶
Introduction¶
This is a physical POD deployed by Fuel installer (Brahmputra).
Additional Requirements¶
Server Specifications¶
Jump Host
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPNFV-jump | SuperMicro | SYS-5018R-WR | E5-2630v3 x1 | 32 GB | SATA 7.2krpm 2TB x1 |
| Hostname | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPNFV-jump | IF0: 0c:c4:7a:6c:a2:b2 VLAN untagged Public IF1: 0c:c4:7a:6c:a2:b3 VLAN 10{2-5} Admin/Mgmt/Private | NIC Model: Intel I350 |
Compute Nodes
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| node-9 | FUJITSU | RX2530 M1 | E5-2630v3 x1 | 32 GB | SATA 7.2krpm 2TB x2 SSD 100GB x1 | |
| node-10 | FUJITSU | RX2530 M1 | E5-2630v3 x1 | 32 GB | SATA 7.2krpm 2TB x2 SSD 100GB x1 | |
| node-11 | FUJITSU | RX2530 M1 | E5-2630v3 x1 | 32 GB | SATA 7.2krpm 2TB x2 SSD 100GB x1 | |
| node-12 | FUJITSU | RX2530 M1 | E5-2630v3 x1 | 32 GB | SATA 7.2krpm 2TB x2 SSD 100GB x1 |
| Hostname | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| node-9 | IF0: 90:1b:0e:6b:e8:a8 VLAN untagged Admin IF1: 90:1b:0e:6b:e8:a9 VLAN untagged Mgmt IF2: 90:1b:0e:6b:e8:aa VLAN untagged Public IF3: 90:1b:0e:6b:e8:ab VLAN untagged Private | IF4: 90:1b:0e:6d:09:71 VLAN untagged Storage IF5: 90:1b:0e:6d:09:72 VLAN untagged Storage | NIC Models: (1GbE) Emulex Skyhawk (10GbE) Intel 82599E | |
| node-10 | IF0: 90:1b:0e:6b:e3:00 VLAN untagged Admin IF1: 90:1b:0e:6b:e3:01 VLAN untagged Mgmt IF2: 90:1b:0e:6b:e3:02 VLAN untagged Public IF3: 90:1b:0e:6b:e3:03 VLAN untagged Private | IF4: 90:1b:0e:6d:09:5f VLAN untagged Storage IF5: 90:1b:0e:6d:09:60 VLAN untagged Storage | NIC Models: (1GbE) Emulex Skyhawk (10GbE) Intel 82599E | |
| node-11 | IF0: 90:1b:0e:6b:e5:b4 VLAN untagged Admin IF1: 90:1b:0e:6b:e5:b5 VLAN untagged Mgmt IF2: 90:1b:0e:6b:e5:b6 VLAN untagged Public IF3: 90:1b:0e:6b:e5:b7 VLAN untagged Private | IF4: 90:1b:0e:6d:09:6f VLAN untagged Storage IF5: 90:1b:0e:6d:09:70 VLAN untagged Storage | NIC Models: (1GbE) Emulex Skyhawk (10GbE) Intel 82599E | |
| node-12 | IF0: 90:1b:0e:6b:e2:bc VLAN untagged Admin IF1: 90:1b:0e:6b:e2:bd VLAN untagged Mgmt IF2: 90:1b:0e:6b:e2:be VLAN untagged Public IF3: 90:1b:0e:6b:e2:bf VLAN untagged Private | IF4: 90:1b:0e:6d:08:31 VLAN untagged Storage IF5: 90:1b:0e:6d:08:32 VLAN untagged Storage | NIC Models: (1GbE) Emulex Skyhawk (10GbE) Intel 82599E |
Switches
| Node | Hardware |
|---|---|
| Switch 1 (for each network except storage) | Juniper EX3300-24T |
| Switch 2 (for storage) | Mellanox SX1024 |
Subnet Allocations
| Network name | Address | Mask | Gateway | VLAN id |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public | 192.168.25.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.25.254 | 103 |
| Fuel Admin | 192.168.103.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.103.1 | 103 |
| Fuel Mangement | 192.168.104.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.104.1 | 104 |
| Fuel Public | 192.168.105.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.105.1 | 105 |
| Fuel Private | 192.168.106.0 | 255.255.255.0 | Untagged | |
| Fuel Storage | 192.168.107.0 | 255.255.255.0 | Untagged |
VPN Users¶
| Name | Project | Role | Notes | |
| Ryota Mibu | r-mibu@cq.jp.nec.com | Doctor | Project Lead |
Firewall Rules¶
| Port(s) | Service | Notes |
POD Topology¶

5.4.3. POD: ool-virtual1¶
Introduction¶
This is a virtual POD deployed by Apex installer (master/Colorado). This POD is built on one machine placed next to machines of the physical POD (ool-pod1). Controller and compute nodes are VM.
Additional Requirements¶
Server Specifications¶
Jump Host
Compute Nodes
| Machine | Hostname | Hardware |
|---|---|---|
| Virtual POD | ool-virtual1 | FUJITSU PRIMERGY RX2530 M1 |
| FUJITSU PRIMERGY RX2530 M1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Xeon E5-2630v3 | x1 |
| RAM | 32GB | |
| HDD | SATA 7.2krpm 2TB | x2 |
| SSD | 100GB | x1 |
| 1000BASE-T | Emulex Skyhawk | x2 |
| 10GBASE-T | Intel 82599E | x2 |
| BMC | x1 | |
| Hostname | IF# | BW | MAC | IF in OS | Role |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ool-virtual1 | IF0 | 1Gb | 90:1b:0e:6b:e5:d8 | eno1 | Admin |
| ool-virtual1 | IF1 | 1Gb | 90:1b:0e:6b:e5:d9 | eno2 | Mgmt |
| ool-virtual1 | IF2 | 1Gb | 90:1b:0e:6b:e5:da | eno3 | Public |
| ool-virtual1 | IF3 | 1Gb | 90:1b:0e:6b:e5:db | eno4 | Private |
| ool-virtual1 | IF4 | 1Gb | 90:1b:0e:6d:08:f5 | ens2f0 | Storage |
| ool-virtual1 | IF5 | 1Gb | 90:1b:0e:6d:08:f6 | ens2f1 | Storage |
Subnet Allocations in the host
| Network name | Address | Mask | Gateway | VLAN id |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admin | 192.0.2.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.103.1 | Untagged |
| Public | 192.168.37.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.105.1 | Untagged |
| Private | 11.0.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | Untagged | |
| Storage | 12.0.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | Untagged |
VPN Users¶
| Name | Project | Role | Notes | |
| Ryota Mibu | r-mibu@cq.jp.nec.com | Doctor | Project Lead |
Firewall Rules¶
| Port(s) | Service | Notes |
POD Topology¶
5.4.4. OOL Inventory File¶
import pod1_inventory.yaml
5.5. Orange Paris Pharos Lab and Configuration Files¶
5.5.1. Lab Specification Template¶
Introduction¶
Orange is hosting an OPNFV test lab at Chatillon (near Paris) facility. The test lab would host baremetal servers for the use of OPNFV community as part of the OPNFV Pharos Project.
- The Orange Paris lab consist of 1 POD
- POD for Fuel
Lab Resources¶
| POD Name | Project(s) | Project Lead(s) | Email(s) | POD Role | Status | Notes |
| opnfv-integ | Dev/test | Active |
- POD Name: Use consistent naming / numbering to avoid confusion. Hyperlinked to POD description.
- POD Role: CI stable, CI latest, Dev/test, Stand-alone, Virtual, ...
- Status: Assigned, Configuring, Active, Troubleshooting, Available, ...
Acceptable Usage Policy¶
Define lab user policies and expectations
Remote Access Infrastructure¶
The Orange Paris OPNFV test lab is free to use for the OPNFV community.
A VPN is used to provide access to the Orange Paris Testlab.
To access the Testlab, please contact Auboin Cyril (cyril.auboin@orange.com) with the following details: * Name
- Organization
- Purpose of using the labs
- Dates start / end
Processing the request can take 3-4 business days.
Remote Access Procedure¶
Define lab process for requesting access to the lab (e.g. VPN guide, how to modify BIOS settings, etc.)
Lab Documentation¶
List lab specific documents here
Lab Topology¶
Provide a diagram showing the network topology of lab including lights-out network. Any security sensitive details should not be exposed publically. The following diagram is an example only.

5.5.2. POD Specification Template¶
Introduction¶
Orange is hosting an OPNFV test lab at Chatillon (near Paris) facility. The test lab would host 4 (1 controller and 3 computes) baremetal servers for the use of OPNFV community as part of the OPNFV Pharos Project.
Version: Brahmaputra Installer: Fuel (with Ceph)
Additional Requirements¶
Server Specifications¶
Switch
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory | Local storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| pod1- switch | JUNIPER | EX-4550 | 750-045407 | 172.31.2.254 CC:E1:7F:86:38:80 | 32 ports |
Jump Host
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory | Local storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| pod1- jump-host | DELL | Proliant DL 360e Gen8 | CZJ40901PV |
E5-2430 v2.2 2,5Ghz 24 core |
16 GB | 300GB SAS 300GB SAS | IF0: 172.31.13.5 |
Firewall
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory | Local storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| pod1- firewall | IBM | @Server xSerie 336 | KKTVY4M | Intel Xeon | 4 GB | 36GB SATA 36GB SATA | IF0: 161.105.211.2 |
Controller Node
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory | Local storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| pod1-ctrl1 | HP | Proliant DL 360e Gen8 | CZJ40901PT |
|
16GB | 300GB SAS 300GB SAS |
|
Compute Nodes
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory | Local storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| pod1-node1 | DELL | R730 | 8F3J642 | Intel Xeon E5-2603 v3
|
128GB (8x16GB) 1600Mhz | 250GB SATA 480GB SSD 480GB SSD |
|
|||
| pod1-node2 | HP | Proliant DL 360e Gen8 | CZJ40901PS |
|
16GB | 300GB SAS 300GB SAS |
|
|||
| pod1-node3 | DELL | R730 | FG3J642 | Intel Xeon E5-2603 v3
|
128GB (8x16GB) 1600Mhz | 256GB SATA 480GB SSD 480GB SSD |
|
Users¶
| Name | Company | Role | Notes | |
Firewall Rules¶
| Port(s) | Service | Note |
| 22, 43, 80 | Jenkins CI |
POD Topology¶
Provide a diagram showing the network topology of the POD. Any security sensitive details should not be exposed publically and can be stored in the secure Pharos repo. The following diagram is an example only.

5.6. Spirent Virtual Cloud Test Lab¶
A community provided metal resource hosted at Nephoscale, leveraged for SDN/NFV public testing and OpenDaylight, OpenStack, OPNFV projects.
Spirent VCT Lab is currently working on 3 different OpenStack environments each one of them deployed on different hardware configuration:
- OpenStack Juno - 2014.2.2 release (CentOS 7, 20 Cores, 64 GB RAM, 1 TB SATA, 40 Gbps)
- OpenStack Juno - 2014.2.2 release (Ubuntu 14.04, 8 cores, 32 GB RAM, 500 GB SATA, 10 Gbps)
- OpenStack Icehouse - 2014.1.3 release
- OpenStack Icehouse - 2014.1.3 release
There are a number of different networks referenced in the VPTC Design Blueprint.
- Public Internet – 1 g
- Private Management – 1g
- Mission Clients – 10g
- Mission Servers – 10g
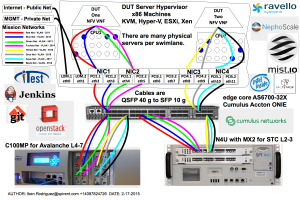
These can be added or removed as specified by the test methodology. There are 8 x 10 gige SFP+ ports available on a typical C100MP used for Avalanche Layer 4-7 testing. The N4U offers 2 x 40 gige QSFP+ ports with the MX-2 Spirent Test Center Layer 2-3 testing. There are 2 x Cumulus switches with 32 ports of 40 gige QSFP+ ports for a total capacity of 256 ports of 10 gige. We use QSFP+ to SFP+ break out cables to convert a single 40 gige port into 4 x 10 gige ports. Together these offer a flexible solution to allow up to 8 simultaneous tests to take place with physical traffic generators at the same time. Assuming a 10 to 1 oversubscription ratio we could handle 80 community users with the current environment.
For example:
- An 80 Gbps test would need 4 port pairs of 10 gige each and require 8 mission networks.
- Multiple clients sharing common test hardware might have dedicated management networks for their DUTs yet communicate with the APIs and Management services via a shared DMZ network protected by a firewall.
- SSL and IPSec VPN will typically be leveraged to connect networks across the untrusted Internet or other third party networks.
- Stand-alone DUT servers using STCv and AVv traffic generators could easily scale to hundreds of servers as needed.
5.7. ZTE SH Pharos Lab Configuration Files¶
5.7.1. ZTE SH Lab Specification¶
Introduction¶
ZTE SH Pharos lab currently has three PODs available in Shanghai. Each POD has 5 servers, 3 controller nodes and 2 computer nodes. These PODs are dedicated for use by Production/CI. These PODs focus scenarios related with test projects, installer projects and performance enhancement projects, such as KVM, OVS, FDS, etc.
Scenarios planned are list here:
- os-nosdn-kvm-ha
- os-nosdn-kvm_ovs-ha
Scenarios are defined in Colorado Scenario Status
Lab Resources¶
| POD Name | Project(s) | PTL(s) | Email(s) | POD Role | Status | Notes |
| POD1 | FUEL | Gregory Elkinbard | gelkinbard@mirantis.com | CI: latest | Active | Yardstick Funtest Doctor Parser |
| POD2 | FUEL | Gregory Elkinbard | gelkinbard@mirantis.com | CI: latest | Active | Qtip |
| POD3 | FUEL | Gregory Elkinbard | gelkinbard@mirantis.com | CI: latest | Active | NFV-KVM OVSNFV |
Acceptable Usage Policy¶
Resources located in OPNFV ZTE SH lab shall only be used for CI, infra setup/configuration and troubleshooting purposes. No development work is allowed in these PODs.
Remote Access Infrastructure¶
ZTE SH lab provide the OpenVPN access for you.
Remote Access Procedure¶
Access to this environment can be granted by sending an e-mail to: yangyang1@zte.com.cn.
Subject: opnfv zte-pod[1-3] access.
The following information should be provided in the request:
Full name:
E-mail:
Organization:
Why is access needed:
How long is access needed:
What specific Host will be accessed:
What support is needed from zte admin:
Once access requirment is approved, the instructions for setting up VPN access will be send to you by mail.
Lab Documentation¶
Lab Topology¶
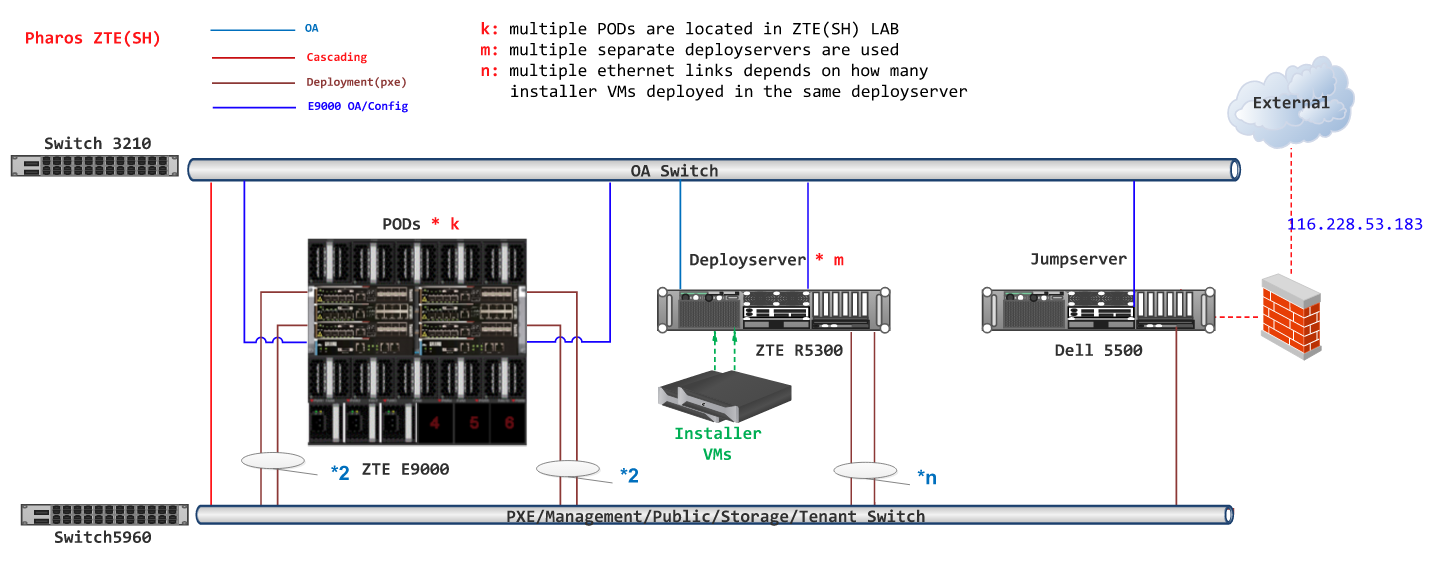
All the PODs share the same Jump Host for only one public IP address is allocated for ZTE Pharos Lab. Deploy servers are separated from Jump Host. Each POD has itsown Deploy Server.
Jump Host
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory (GB) | Local Storage | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| Rabbit | HP | 5500 | X5647x2 | 24 | 250GB SAS 2 TB HDD | IF0: a0:36:9f:00:11:34/ 192.168.1.1/ native vlan/OA IF1: a0:36:9f:00:11:35/ 172.10.0.1/ vlan 103/Public 172.20.0.1/ vlan 113/Public 172.60.0.1/ vlan 163/Public 172.70.0.1/ vlan 173/Public IF2: a0.36:9:00:11:37/ 116.228.53.183/ native vlan/ Internet |
5.7.2. ZTE POD1 Specification¶
Introduction¶
POD1(means ZTE-POD1) uses Fuel as the installer and performs os-odl_l2-nofeature-ha CI latest verification. Currently, test projects such as Yardstick, Functest are performing daily CI tasks. Fueature projects such as Doctor, Parser will perform daily and verify CI tasks.
Additional Requirements¶
Server Specifications¶
Jump Host
POD1 share the same Jump Host in the lab.
Deploy server
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory (GB) | Local Storage | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| Jellyfish | ZTE | R5300 | 277662500093 | E5-2620x2 | 128 | 600GB SAS 4 TB HDD | IF0: 74:4a:a4:00:91:b3/ 10.20.6.1/ native vlan/PXE IF1: 74:4a:a4:00:91:b4/ 10.20.7.1/ native vlan/PXE |
Nodes/Servers
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory (GB) | Local Storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| node1 | ZTE | E9000 | 701763100025 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.101 74:4a:a4:00:cf:d9 zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:cf:dc native vlan 160/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:b0:e1 vlan 161/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:b0:e2 vlan 162/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:b0:dd vlan 1120/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:b0:de vlan 163/ public | |
| node2 | ZTE | E9000 | 701763100224 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.102 74:4a:a4:00:ce:cb zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:ce:ce native vlan 160/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:ad vlan 161/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:ae vlan 162/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:a9 vlan 1120/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:aa vlan 163/ public | |
| node3 | ZTE | E9000 | 701763100064 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.103 74:4a:a4:00:cf:55 zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:cf:58 native vlan 160/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:ab vlan 161/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:ac vlan 162/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:af vlan 1120/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:b0 vlan 163/ public | |
| node4 | ZTE | E9000 | 289842100103 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.104 74:4a:a4:00:49:81 zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:49:84 native vlan 160/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:b1:a5 vlan 161/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:b1:a6 vlan 162/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:b1:b1 vlan 1120/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:b1:b2 vlan 163/ public | |
| node5 | ZTE | E9000 | 701763100220 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.105 74:4a:a4:00:ce:bf zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:ce:c2 native vlan 160/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:8d vlan 161/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:8e vlan 162/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:9b vlan 1120/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:9c vlan 163/ public |
Subnet allocations
| Network name | Address | Mask | Gateway | VLAN id |
| Public | 172.60.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.60.0.1 | 163 |
| Fuel Admin/PXE | 10.20.6.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.20.6.2 | native vlan 160 |
| Fuel Mangement | 192.168.61.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 161 | |
| Fuel Storage | 192.168.62.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 162 |
VPN Users¶
| Name | Project | Role | Notes | |
Firewall Rules¶
| Port(s) | Service | Note |
| 1194(OpenVPN) | Jenkins |
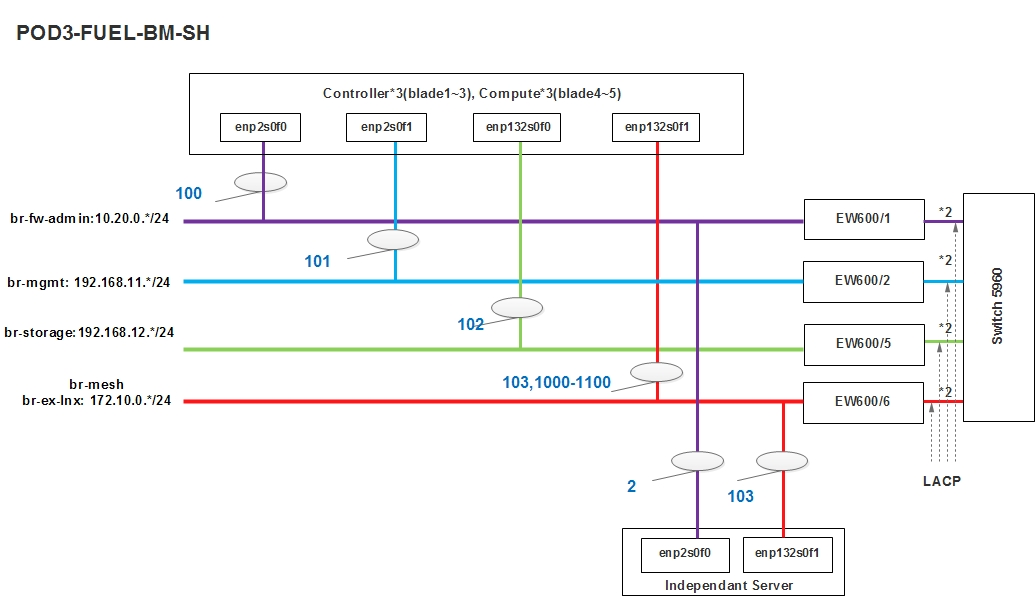
POD Topology¶
5.7.3. ZTE POD2 Specification¶
Introduction¶
POD2(means ZTE-POD2) uses Fuel as the installer and performs os-odl_l2-nofeature-ha CI latest verification. Qtip daily CI task will be migrated from POD1 to POD2. Qtip is also working on integration with Yardstick umbrella project.
Additional Requirements¶
Server Specifications¶
Jump Host
POD2 share the same Jump Host in the lab.
Deploy Server
POD2 share the same Deploy Server with POD1.
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory (GB) | Local Storage | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| Jellyfish | ZTE | R5300 | 277662500093 | E5-2620x2 | 128 | 600GB SAS 4 TB HDD | IF0: 74:4a:a4:00:91:b3/ 10.20.6.1/ native vlan/PXE IF1: 74:4a:a4:00:91:b4/ 10.20.7.1/ native vlan/PXE |
Nodes/Servers
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory (GB) | Local Storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| node1 | ZTE | E9000 | 701763100114 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.106 74:4a:a4:00:cd:6f zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:cd:72 native vlan 170/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:b0:e9 vlan 171/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:b0:ea vlan 172/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:b0:eb vlan 1130/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:b0:ec vlan 173/ public | |
| node2 | ZTE | E9000 | 701360500105 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.107 74:4a:a4:00:ca:c9 zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:ca:cc native vlan 170/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:a3 vlan 171/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:a4 vlan 172/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:99 vlan 1130/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:9a vlan 173/ public | |
| node3 | ZTE | E9000 | 701360500026 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.108 74:4a:a4:00:cd:0f zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:cd:12 native vlan 170/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:9d vlan 171/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:9e vlan 172/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d3:15 vlan 1130/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d3:16 vlan 173/ public | |
| node4 | ZTE | E9000 | 701763100099 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.109 74:4a:a4:00:cf:3d zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:cf:40 native vlan 170/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:a5 vlan 171/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:a6 vlan 172/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:a7 vlan 1130/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d6:a8 vlan 173/ public | |
| node5 | ZTE | E9000 | 701763100018 | E5-2650x2 | 128 | 600GB*2 HDD | 192.168.1.110 74:4a:a4:00:ce:d1 zteroot/superuser | ens4f0: 74:4a:a4:00:ce:d4 native vlan 170/PXE | ens12f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d2:c3 vlan 171/ management ens12f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d2:c4 vlan 172/ storage ens44f0: 74:4a:a4:00:d2:c1 vlan 1130/ private ens44f1: 74:4a:a4:00:d2:c2 vlan 173/ public |
Subnet allocations
| Network name | Address | Mask | Gateway | VLAN id |
| Public | 172.70.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.70.0.1 | 173 |
| Fuel Admin | 10.20.7.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.20.7.1 | native vlan 170 |
| Fuel Mangement | 192.168.71.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 171 | |
| Fuel Storage | 192.168.72.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 172 |
VPN Users¶
| Name | Project | Role | Notes | |
Firewall Rules¶
| Port(s) | Service | Note |
| 1194(OpenVPN) | Jenkins |
POD Topology¶

5.7.4. ZTE SH POD3 Specification¶
Introduction¶
POD3(means ZTE-POD3) uses Fuel as the installer and performs os-nosdn-kvm-ha CI latest verification. Feature projects like NFV-KVMV, OVSNFV will be run in this POD.
Additional Requirements¶
Server Specifications¶
Jump Host
POD3 share the same Jump Host in the lab.
Deploy Server
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory (GB) | Local Storage | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| Spider | ZTE | R5300 | 210077307607 | E5-2609x1 | 32 | 600GB SAS 1.2TB SCSI | IF0: 74:4a:a4:00:21:0b/ 10.20.0.1/ native vlan/PXE IF1: 74:4a:a4:00:21:0c/ 10.20.1.1/ native vlan/PXE |
Compute Nodes
| Hostname | Vendor | Model | Serial Number | CPUs | Memory (GB) | Local Storage | Lights-out network (IPMI): IP/MAC, U/P | 1GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | 10GbE: NIC#/IP MAC/VLAN/Network | Notes |
| node1 | ZTE | E9000 | 289016500203 | E5-2670x2 | 64 | 600GB HDD | 192.168.1.32 0c:12:62:e4:bf:de zteroot/superuser | enp2s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:0b:85 vlan 100/ Admin(PXE) enp2s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:0b:86 vlan 101/ mgmt enp132s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:0b:87 vlan 102/ storage enp132s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:0b:88 vlan 103/ public vlan 1020/ private | ||
| node2 | ZTE | E9000 | 289016500197 | E5-2670x2 | 64 | 600GB HDD | 192.168.1.33 0C:12:62:E4:C0:33 zteroot/superuser | enp2s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:5d vlan 100/ Admin(PXE) enp2s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:5e vlan 101/ mgmt enp132s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:5f vlan 102/ storage enp132s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:60 vlan 103/ public vlan 1020/ private | ||
| node3 | ZTE | E9000 | 289016500003 | E5-2670x2 | 64 | 600GB HDD | 192.168.1.34 74:4A:A4:00:30:93 zteroot/superuser | enp2s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:35 vlan 100/ Admin(PXE) enp2s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:36 vlan 101/ mgmt enp132s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:37 vlan 102/ storage enp132s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:38 vlan 103/ public vlan 1020/ private | ||
| node4 | ZTE | E9000 | 289016500105 | E5-2670x2 | 64 | 600GB HDD | 192.168.1.35 0C:12:62:E4:C0:42 zteroot/superuser | enp2s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:69 vlan 100/ Admin(PXE) enp2s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:6a vlan 101/ mgmt enp132s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:6b vlan 102/ storage enp132s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:6c vlan 103/ public vlan 1020/ private | ||
| node5 | ZTE | E9000 | 289016500195 | E5-2670x2 | 64 | 600GB HDD | 192.168.1.36 74:4A:A4:00:30:43 zteroot/superuser | enp2s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:6d vlan 100/ Admin(PXE) enp2s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:6e vlan 101/ mgmt enp132s0f0: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:6f vlan 102/ storage enp132s0f1: 74:4a:a4:00:5c:70 vlan 103/ public vlan 1020/ private |
Subnet allocations
| Network name | Address | Mask | Gateway | VLAN id |
| Public | 172.10.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.10.0.1 | 103 |
| Fuel Admin/PXE | 10.20.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.20.0.1 | native valn 100 |
| Fuel Mangement | 192.168.11.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 101 | |
| Fuel Storage | 192.168.12.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 102 |
VPN Users¶
| Name | Project | Role | Notes | |
Firewall Rules¶
| Port(s) | Service | Note |
| 5000(OpenVPN) | Jenkins |
POD Topology¶