Doctor scenario¶
Platform overview¶
Doctor platform provides these features in Colorado Release:
- Immediate Notification
- Consistent resource state awareness for compute host down
- Valid compute host status given to VM owner
These features enable high availability of Network Services on top of the virtualized infrastructure. Immediate notification allows VNF managers (VNFM) to process recovery actions promptly once a failure has occurred.
Consistency of resource state is necessary to execute recovery actions properly in the VIM.
Ability to query host status gives VM owner the possibility to get consistent state information through an API in case of a compute host fault.
The Doctor platform consists of the following components:
- OpenStack Compute (Nova)
- OpenStack Telemetry (Ceilometer)
- OpenStack Alarming (Aodh)
- Doctor Inspector
- Doctor Monitor
Note
Doctor Inspector and Monitor are sample implementations for reference.
You can see an overview of the Doctor platform and how components interact in Fig. 1.
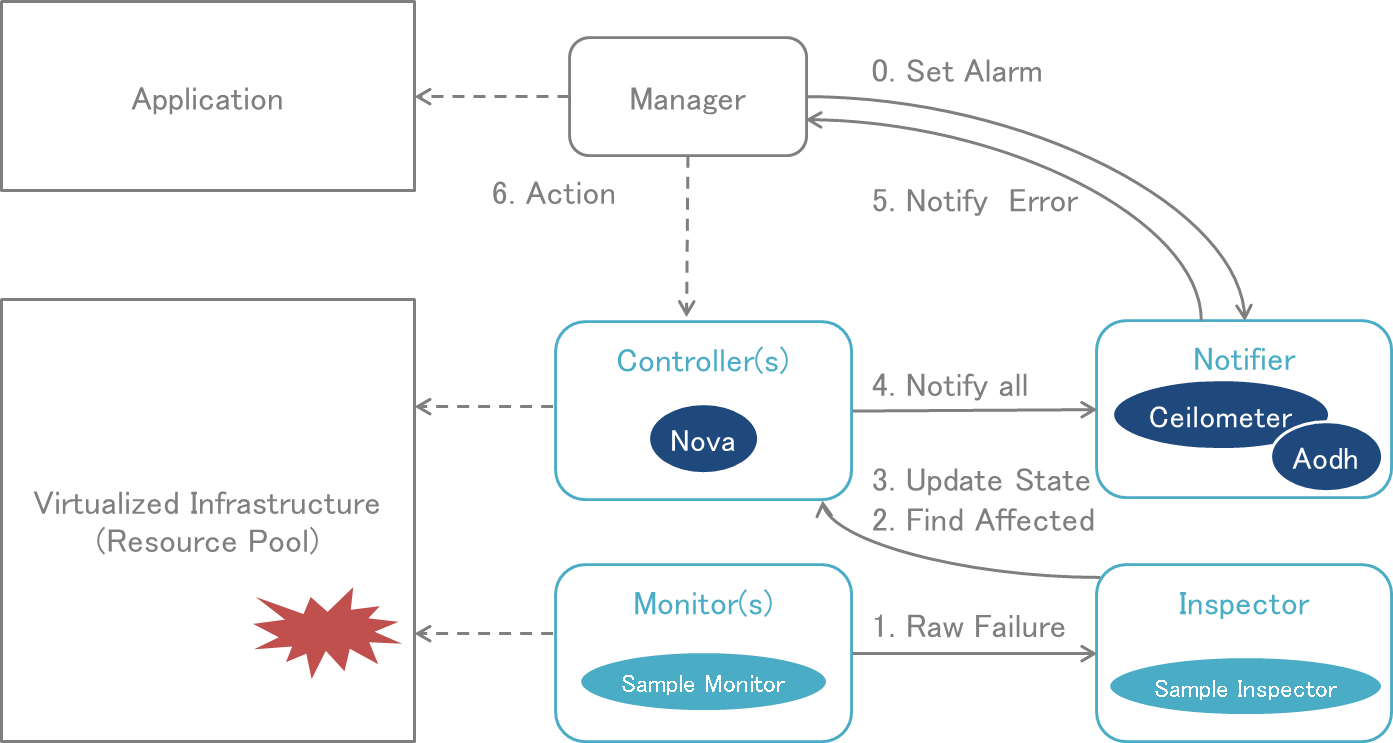
Doctor platform and typical sequence (Colorado)¶
Detailed information on the Doctor architecture can be found in the Doctor requirements documentation: http://artifacts.opnfv.org/doctor/colorado/requirements/05-implementation.html
Use case¶
- A consumer of the NFVI wants to receive immediate notifications about faults in the NFVI affecting the proper functioning of the virtual resources. Therefore, such faults have to be detected as quickly as possible, and, when a critical error is observed, the affected consumer is immediately informed about the fault and can switch over to the STBY configuration.
The faults to be monitored (and at which detection rate) will be configured by the consumer. Once a fault is detected, the Inspector in the Doctor architecture will check the resource map maintained by the Controller, to find out which virtual resources are affected and then update the resources state. The Notifier will receive the failure event requests sent from the Controller, and notify the consumer(s) of the affected resources according to the alarm configuration.
Detailed workflow information is as follows:
- Consumer(VNFM): (step 0) creates resources (network, server/instance) and an event alarm on state down notification of that server/instance
- Monitor: (step 1) periodically checks nodes, such as ping from/to each dplane nic to/from gw of node, (step 2) once it fails to send out event with “raw” fault event information to Inspector
- Inspector: when it receives an event, it will (step 3) mark the host down (“mark-host-down”), (step 4) map the PM to VM, and change the VM status to down
- Controller: (step 5) sends out instance update event to Ceilometer
- Notifier: (step 6) Ceilometer transforms and passes the event to Aodh, (step 7) Aodh will evaluate event with the registered alarm definitions, then (step 8) it will fire the alarm to the “consumer” who owns the instance
- Consumer(VNFM): (step 9) receives the event and (step 10) recreates a new instance
Test case¶
Functest will call the “run.sh” script in Doctor to run the test job.
Currently, only ‘Apex’ and ‘local’ installer are supported. The test also can run successfully in ‘fuel’ installer with the modification of some configurations of OpenStack in the script. But still need ‘fuel’ installer to support these configurations.
The “run.sh” script will execute the following steps.
Firstly, get the installer ip according to the installer type. Then ssh to the installer node to get the private key for accessing to the cloud. As ‘fuel’ installer, ssh to the controller node to modify nova and ceilometer configurations.
Secondly, prepare image for booting VM, then create a test project and test user (both default to doctor) for the Doctor tests.
Thirdly, boot a VM under the doctor project and check the VM status to verify that the VM is launched completely. Then get the compute host info where the VM is launched to verify connectivity to the target compute host. Get the consumer ip according to the route to compute ip and create an alarm event in Ceilometer using the consumer ip.
Fourthly, the Doctor components are started, and, based on the above preparation, a failure is injected to the system, i.e. the network of compute host is disabled for 3 minutes. To ensure the host is down, the status of the host will be checked.
Finally, the notification time, i.e. the time between the execution of step 2 (Monitor detects failure) and step 9 (Consumer receives failure notification) is calculated.
According to the Doctor requirements, the Doctor test is successful if the notification time is below 1 second.
