Bottlenecks - Testing Guide¶
Project Testing Guide¶
For each test suite, you can either setup test story or test case to run certain test. test story could include several test cases as a set in one configuration file. You could then call the test story or test case by using Bottlencks CLI or Python build process. Details will be shown in the following section.
Brief Introdcution of the Test suites in Project Releases¶
Brahmaputra: rubbos is introduced, which is an end2end NFVI perforamnce tool. Virtual switch test framework(VSTF) is also introduced, which is an test framework used for vswitch performance test.
Colorado: rubbos is refactored by using puppet, which makes it quite flexible to configure with different number of load generator(Client), worker(tomcat). vstf is refactored by extracting the test case’s configuration information.
Danube: posca testsuite is introduced to implementing stress (factor), scenario and tuning test in parametric manner. Two testcases are developed and integrated into community CI pipeline.
Integration Description¶
| Release | integrated installer | Supported Testsuite |
| Brahmaputra | Fuel | Rubbos, VSTF |
| Colorado | Compass | Rubbos, VSTF |
| Danube | Compass | POSCA |
Test suite & Test case Description¶
| Rubbos | rubbos_basic |
| rubbos_TC1101 | |
| rubbos_TC1201 | |
| rubbos_TC1301 | |
| rubbos_TC1401 | |
| rubbos_heavy_TC1101 | |
| vstf | vstf_Ti1 |
| vstf_Ti2 | |
| vstf_Ti3 | |
| vstf_Tn1 | |
| vstf_Tn2 | |
| vstf_Tu1 | |
| vstf_Tu2 | |
| vstf_Tu3 | |
| posca | posca_stress_ping |
posca_stress_traffic (posca_factor_sys_bandwidth) |
Installation of Testsuites¶
- TODO
Setting Up Configrations¶
- TODO
Run Tests Brief¶
- TODO
- More will be shown in the platform overview
POSCA Testsuite Guide¶
POSCA Introduction¶
The POSCA (Parametric Bottlenecks Testing Catalogue) testsuite classifies the bottlenecks test cases and results into 5 categories. Then the results will be analyzed and bottlenecks will be searched among these categories.
The POSCA testsuite aims to locate the bottlenecks in parmetric manner and to decouple the bottlenecks regarding the deployment requirements. The POSCA testsuite provides an user friendly way to profile and understand the E2E system behavior and deployment requirements.
- Goals of the POSCA testsuite:
- Automatically locate the bottlenecks in a iterative manner.
- Automatically generate the testing report for bottlenecks in
- different categories.
- Implementing Automated Staging.
- Scopes of the POSCA testsuite:
- Modeling, Testing and Test Result analysis.
- Parameters choosing and Algorithms.
- Test stories of POSCA testsuite:
- Factor test (Stress test): base test cases that Feature test and Optimization will be
- dependant on.
- Feature test: test cases for features/scenarios.
- Optimization test: test to tune the system parameter.
Detailed workflow is illutrated below. * TODO Add image here
Preinstall Packages¶
- TODO Description of dependent packages
Run POSCA Locally¶
- TO Description of POSCA testing steps
Run POSCA through Community CI¶
- TODO Description of POSCA integrated into CI system
Test Result Description¶
- TODO hwo to access the test result
Rubbos Testsuite Guide¶
Rubbos Introduction¶
Rubbos is a bulletin board benchmark modeled after an online news forum like Slashdot. It is an open source Middleware and an n-tier system model which is used to be deployed on multiple physical node and to measure the whole performacne of OPNFV platform. Rubbos can deploy the Apache, tomcat, and DB. Based on the deployment, rubbos gives the pressure to the whole system. When the system reaches to the peak, the throughput will not grow more. This testcase can help to understand the bottlenecks of OPNFV plantform and improve the performance of OPNFV platform.
Detailed workflow is illutrated below.
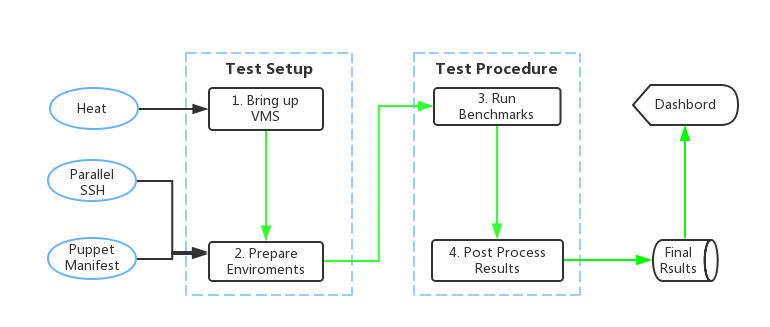
Preinstall Packages¶
There is a need to install some packages before running the rubbos, gcc, gettext, g++, libaio1, libaio-dev, make and git are necessary. When the rubbos runs on the OPNFV community continuous integration(CI) system, the required packages are installed automately as shown in the code repository, which is /utils/infra_setup/vm_dev_setup/packages.conf, besides, the packages can be encapsulated in the images initially. If someone wants to use rubbos locally, he/she has to install them by hand, such as in ubuntu 14.04,
apt-get update
apt-get install gettext
How does Rubbos Integrate into Installers¶
1.Community CI System
Rubbos has been successfully integrated into fuel and compass with NOSDN scenario in OPNFV community CI system.
Heat is used to create 9 instances, which is shown in /utils/infra_setup/heat_template/HOT_create_instance.sh, the 9 instances are used for installing Apache, Tomcat, Mysql, Control, Benchmark and 4 Clients. The tools, such as rubbos, sysstat, oprofile, etc, are installed in these instances to perform the test, the test results are stored in the Benchmark instance initially, then they are copied to the Rubbos_result instance, finally, the test results are transferred to the community dashboard.
There’s a need to store our pakages as large as M bytes or G bytes size, such as the images, jdk, apache-ant, apache-tomcat, etc, the OPNFV community storage system, Google Cloud Storage, is used, the pakages can be downloaded from https://artifacts.opnfv.org/bottlenecks/rubbos.
2.Local Deployment
If someone wants to run the rubbos in his own environment, he/she can keep to the following steps,
2.1 Start up instances by using heat, nova or libvert. In Openstack Environemnt, the heat script can refer /utils/infra_setup/heat_template/HOT_create_instance.sh, if the openstack doesn’t support heat module, the script /utils/infra_setup/create_instance.sh can be used. Without Openstack, there’s a way to set up instances by using libvert, the scripts are shown under the directory /utils/rubbos_dev_env_setup.
The image can be downloaded from the community cloud storage
curl --connect-timeout 10 -o bottlenecks-trusty-server.img
http://artifacts.opnfv.org/bottlenecks/rubbos/bottlenecks-trusty-server.img
2.2 Ssh into the control node and clone the bottlenecks codes to the root directory.
git clone https://git.opnfv.org/bottlenecks /bottlenecks
2.3 Download the packages and decompress them into the proper directory.
curl --connect-timeout 10 -o app_tools.tar.gz
http://artifacts.opnfv.org/bottlenecks/rubbos/app_tools.tar.gz
curl --connect-timeout 10 -o rubbosMulini6.tar.gz
http://artifacts.opnfv.org/bottlenecks/rubbos/rubbosMulini6.tar.gz
tar zxf app_tools.tar.gz -C /bottlenecks/rubbos
tar zxf rubbosMulini6.tar.gz -C /bottlenecks/rubbos/rubbos_scripts
2.4 Ssh into the Control node and run the script
source /bottlenecks/rubbos/rubbos_scripts/1-1-1/scripts/run.sh
2.5 Check the test results under the directory /bottlenecks/rubbos/rubbos_results in Control node. The results are stored in the format of xml, move them to the brower chrome, then you can see the results.
Test Result Description¶
In OPNFV community, the result is shown in the following format
[{'client': 200, 'throughput': 27},
{'client': 700, 'throughput': 102},
{'client': 1200, 'throughput': 177},
{'client': 1700, 'throughput': 252},
{'client': 2200, 'throughput': 323},
{'client': 2700, 'throughput': 399},
{'client': 3200, 'throughput': 473}]
The results are transferred to the community database and a map is drawed on the dashboard. Along with the growth of the number of the client, the throughput grows at first, then meets up with a point of inflexion, which is caused by the bottlenecks of the measured system.
VSTF Testsuite Guide¶
VSTF Introduction¶
VSTF(Virtual Switch Test Framework) is a system-level testing framework in the area of network virtualization, and it could help you estimate the system switch ability and find out the network bottlenecks by main KPIs(bandwidth, latency, resource usage and so on), VSTF owns a methodology to define the test scenario and testcases, Now we could support Tu testcases in the Openstack environment, More scenarios and cases will be added.
VSTF TestScenario¶
- Tu - VM to VM
- Tn - Physical Nic loopback
- TnV - VNF loopback
- Ti - VM to Physical Nic
Pre-install Packages on the ubuntu 14.04 VM¶
VSTF VM Preparation Steps¶
- Create a ubuntu 14.04 VM
- Install dependency inside VM
- Install vstf python package inside VM
VM preparation¶
Install python2.7 version and git
sudo apt-get install python2.7
sudo apt-get install git
Download Bottlenecks package
sudo cd /home/
sudo git clone https://gerrit.opnfv.org/gerrit/bottlenecks
Install the dependency
sudo apt-get install python-pip
sudo pip install --upgrade pip
sudo dpkg-reconfigure dash
sudo apt-get install libjpeg-dev
sudo apt-get install libpng-dev
sudo apt-get install python-dev
sudo apt-get install python-testrepository
sudo apt-get install git
sudo apt-get install python-pika
sudo apt-get install python-oslo.config
sudo pip install -r /home/bottlenecks/vstf/requirements.txt
Install vstf package
sudo mkdir -p /var/log/vstf/
sudo cp -r /home/bottlenecks/vstf/etc/vstf/ /etc/
sudo mkdir -p /opt/vstf/
sudo cd /home/bottlenecks;sudo rm -rf build/
sudo python setup.py install
Image on the Cloud¶
| Name | vstf-image |
|---|---|
| URL | http://artifacts.opnfv.org/bottlenecks/vstf-manager-new.img |
| Format | QCOW2 |
| Size | 5G |
| User | root |
| Passwd | root |
There is a complete vstf image on the cloud ,you could download it and use it to deploy and run cases ,but do not need VM preparation steps.
How is VSTF Integrated into Installers¶
VM requirements¶
| Name | FLAVOR | IMAGE_NAME | NETWORK |
|---|---|---|---|
| vstf-manager | m1.large | vstf-image | control-plane=XX.XX.XX.XX |
| vstf-tester | m1.large | vstf-image | control-plane(eth0)=XX.XX.XX.XX test-plane(eth1)=XX.XX.XX.XX |
| vstf-target | m1.large | vstf-image | control-plane(eth0)=XX.XX.XX.XX test-plane(eth1)=XX.XX.XX.XX |
m1.large means 4U4G for the target image Size 5GB For the network used by VMs,network need two plane ,one plane is control plane and the other plane is test plane.
OPNFV community Usage in the CI system¶
| Project Name | Project Categoty |
|---|---|
| bottlenecks-daily-fuel-vstf-lf-master | bottlenecks |
OPNFV community jenkins Project info
Main Entrance for the ci test:
cd /home/bottlenecks/ci;
bash -x vstf_run.sh
Test on local(Openstack Environment)¶
download the image file
curl --connect-timeout 10 -o /tmp/vstf-manager.img \
http://artifacts.opnfv.org/bottlenecks/vstf-manager-new.img -v
create the image file by the glance
glance image-create --name $MANAGER_IMAGE_NAME \
--disk-format qcow2 \
--container-format bare \
--file /tmp/vstf-manager.img
create the keypair for the image(anyone will be ok)
cd /home/bottlenecks/utils/infra_setup/bottlenecks_key
nova keypair-add --pub_key $KEY_PATH/bottlenecks_key.pub $KEY_NAME
create the vstf three VMs in the openstack by heat
cd /home/bottlenecks/utils/infra_setup/heat_template/vstf_heat_template
heat stack-create vstf -f bottleneck_vstf.yaml
launch the vstf process inside the vstf-manager vstf-tester vstf-target VMs
cd /home/bottlenecks/utils/infra_setup/heat_template/vstf_heat_template
bash -x launch_vstf.sh
edit the test scenario and test packet list in the vstf_test.sh, now support the Tu-1/2/3
function fn_testing_scenario(){
...
local test_length_list="64 128 256 512 1024"
local test_scenario_list="Tu-1 Tu-3"
...
}
launch the vstf script
cd /home/bottlenecks/utils/infra_setup/heat_template/vstf_heat_template
bash -x vstf_test.sh
Test Result Description¶
Result Format¶
For example after the test, The result will display as the following format
{ u'64': { u'AverageLatency': 0.063,
u'Bandwidth': 0.239,
u'CPU': 0.0,
u'Duration': 20,
u'MaximumLatency': 0.063,
u'MinimumLatency': 0.063,
u'MppspGhz': 0,
u'OfferedLoad': 100.0,
u'PercentLoss': 22.42,
u'RxFrameCount': 4309750.0,
u'RxMbps': 198.28,
u'TxFrameCount': 5555436.0,
u'TxMbps': 230.03}}
Option Description¶
| Option Name | Description |
|---|---|
| AverageLatency | The average latency data during the packet transmission (Unit:microsecond) |
| Bandwidth | Network bandwidth(Unit:Million packets per second) |
| CPU | Total Resource Cpu usage(Unit: Ghz) |
| Duration | Test time(Unit: second) |
| MaximumLatency | The maximum packet latency during the packet transmission (Unit:microsecond) |
| MinimumLatency | The maximum packet latency during the packet transmission (Unit:microsecond) |
| MppspGhz | Million Packets per second with per CPU resource Ghz(Unit: Mpps/Ghz) |
| OfferedLoad | The load of network offered |
| PercentLoss | The percent of frame loss rate |
| RxFrameCount | The total frame on Nic rx |
| RxMbps | The received bandwidth per second |
| TxFrameCount | The total frame on Nic rx |
| TxMbps | The send bandwidth per second |
Dashbard guide¶
Scope¶
This document provides an overview of the results of test cases developed by the OPNFV Bottlenecks Project, executed on OPNFV community labs.
OPNFV CI(Continous Integration) system provides automated build, deploy and testing for the software developed in OPNFV. Unless stated, the reported tests are automated via Jenkins Jobs.
Test results are visible in the following dashboard:
- Testing dashboard: uses Mongo DB to store test results and Bitergia for visualization, which includes the rubbos test result, vstf test result.
