Parser Project¶
1. Introduction of Parser Project¶
In NFV, various templates (such as descriptors, records and so on) are utilized to describe the deployment requirements (such as basic VM requirements – vCPU, memory, storage, as well as the NFV acceleration management requirement such as Huge Pages support, SR-IOV, NUMA affinity, DPDK support etc.), the post-instaniation records (such as storage usage report, CPU performance report etc.) or other purposes. However in order to make these templates adaptable and feasible for purpose like deployment orchestration/automation, certain tooling mechanism that provides template translation is necessary.
Project Parser will help to provide such tooling mechanism, by parsing Telecom operators’ descriptors/records into TOSCA/CAMP templates and then further translate TOSCA/CAMP templates into certain common templates, which could be used in IaaS orchestration projects like OpenStack Heat.
For Release B, Parser offers the following capabilities:
- Integration of Heat-Translator Liberty release code. (both heat in-tree code and standalone package are provided)
- Yang2Tosca module which offers the capability to translate yang based scriptors to tosca formate templates. Users could further use Heat-translator module to translate this tosca template to Heat Orchestration template. Yang2Tosca module could be installed seperately after user installed OPNFV B release platform.
- The “parser_new_keywords” document demonstrate a set of keywords concluded by Parser team that need to be supported in tosca to heat translation. However it should be noted that these keywords only serve as a roadmap. We will start from Release C to indicate which specific set of keywords are supported in Parser.
- The “vRNC_tosca_intro” document describes Parser’s use case analysis on vRNC scenario. The “example” folder contains examples of tosca-nfv standard and vRNC scenario. See also https://wiki.opnfv.org/parser .
For Release C, Parser offers additional capabilities:
- Policy2Tosca module which enables policy related fields in tosca could be translated into heat orchestration template correctly. Policy2Tosca module could be installed seperately after user installed OPNFV C release platform.
- Tosca2Heat enhancements which includes a set of feature addons (such as substitution mapping)
for OpenStack tosca-parser module which is integrated in the OPNFV C release platform.
- Additional testing support.
2. Parser YANG2TOSCA¶
2.1. Overview¶
Parser is an open source project and licensed under Apache 2. Parser will help to provide a tooling mechanism, by parsing Telecom operators’ VNF descriptors (YANG templates) into TOSCA templates and then further translate TOSCA templates into certain common templates, which could be used in IaaS orchestration projects like OpenStack Heat.
2.2. Prerequisites¶
Parser requires the following to be installed.
2.2.1. 1. PYANG¶
Please follow the below installation steps.
Step 1: Clone pyang tool or download the zip file from the following link.
git clone https://github.com/mbj4668/pyang.git
OR
wget https://github.com/mbj4668/pyang/archive/master.zip
Step 2: Change directory to the downloaded directory and run the setup file.
cd pyang
python setup.py
2.2.2. 2. python-lxml¶
Please follow the below installation link. http://lxml.de/installation.html
2.3. Installation¶
Please follow the below installation steps to install parser.
Step 1: Clone the parser project.
git clone https://gerrit.opnfv.org/gerrit/parser
2.4. Execution¶
Step 1: Change directory to where the scripts are present.
cd parser/yang2tosca
- Step 2: Copy the YANG file which needs to be converted into TOSCA to
- current (parser/yang2tosca) folder.
Step 3: Run the python script “parser.py” with the YANG file as an input option.
python parser.py -n "YANG filename"
Example:
python parser.py -n example.yaml
- Step 4: Verify the TOSCA YAMl which file has been created with the same name
- as the YANG file with a “_tosca” suffix.
cat "YANG filename_tosca.yaml"
Example:
cat example_tosca.yaml
3. Parser POLICY2TOSCA¶
3.1. Overview¶
Parser is an open source project and licensed under Apache 2. Parser will help to provide a tooling mechanism, by parsing Telecom operators’ VNF descriptors (YANG templates) into TOSCA templates and then further translate TOSCA templates into certain common templates, which could be used in IaaS orchestration projects like OpenStack Heat.
3.2. Prerequisites¶
Parser - POLICY2TOSCA requires the following to be installed.
3.2.1. 1. cliff¶
Install cliff with the following links. :: - install <http://docs.openstack.org/developer/cliff/install.html> or - demoapp <http://docs.openstack.org/developer/cliff/demoapp.html>
3.3. Installation¶
Please follow the below installation steps to install parser - POLICY2TOSCA.
Step 1: Clone the parser project.
git clone https://gerrit.opnfv.org/gerrit/parser
Step 2: Install the policy2tosca module.
cd parser/policy2tosca
python setup.py install
3.4. Execution¶
Step 1: To see a list of commands available.
policy2tosca --help
Step 2: To see help for an individual command, include the command name on the command line
policy2tosca help <service>
Step 3: To inject/remove policy types/policy definitions provide the TOSCA file as input to policy2tosca command line.
policy2tosca <service> [arguments]
Example:
policy2tosca add-definition --policy_name rule2 --policy_type tosca.policies.Placement.Geolocation --description "test description" --properties region:us-north-1,region:us-north-2,min_inst:2 --targets VNF2,VNF4 --metadata "map of strings" --triggers "1,2,3,4" --source example.yaml
Step 4: Verify the TOSCA YAMl updated with the injection/removal executed.
cat "<source tosca file>"
Example:
cat example_tosca.yaml
4. New Parser keywords¶
4.1. 1.NFV-tosca new keywords¶
All keywords in nfv tosca are not implemented in code, and will be implemented by parser.
4.1.1. 1.1 Nodes types¶
4.1.1.1. Basic types¶
- tosca.nodes.nfv.VDU
- tosca.nodes.nfv.CP
- tosca.nodes.nfv.VL
4.1.1.2. Extend types¶
- tosca.nodes.nfv.VL.ELine
- tosca.nodes.nfv.VL.ELAN
- tosca.nodes.nfv.VL.ETree
- tosca.nodes.nfv.FP
4.1.2. 1.2 Capability types¶
4.1.2.1. Basic types¶
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.VirtualBindable
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.VirtualLinkable
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.HA.ActiveActive
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.HA.ActivePassive
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.Metric
4.1.2.2. Extend types¶
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.Forwarder
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.CPU_extension
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.Memory_extension
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.Hypervisors
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.PCIe
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.network.Interfaces
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.network.Virtual_switches
- tosca.capabilities.nfv.Storage
4.1.3. 1.3 Relationship types¶
4.1.3.1. Basic types¶
- tosca.relationships.nfv.VirtualBindsTo
- tosca.relationships.nfv.VirtualLinksTo
- tosca.relationships.nfv.HA
- tosca.relationships.nfv.Monitor
4.1.3.2. Extend types¶
- tosca.relationships.nfv.ForwardsTo
4.1.4. 1.4 Group Types¶
- tosca.groups.nfv.VNFFG
4.2. 2.Simple-tosca new keywords¶
Some keywords are only defined in tosca simple profile,but are not supported in tosca-paser, and some keywords such as “policy type”, are not yet defined completely so far.
4.2.1. 2.1 topology template keyname¶
“substitution_mappings” syntax
An optional declaration that exports the topology template as an impletmentation of a node type, which is not supported by tosca-parser.
5. 1. vRNC Topology¶
The simple vRNC topology is shown below: Fig. 5.1
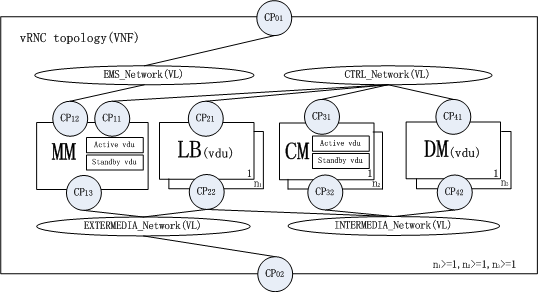
vRNC Topology¶
- vRNC includes four networks: EMS_network, CTRL_network, Intermedia_network and extermedia_network;
- vRNC includes four node types: MM, LB, CM and DM;
- MM: Stands for Maintain Module, which links to EMS_network, CTRL_network and extermedia_network. It composes of active vdu and standby vdu.
- CM: Stands for Control Module, which links to CTRL_network and intermedia_network. All CM nodes form resource pool and each node composes of active vdu and standby vdu.
- DM: Stands for Data Module, which links to CTRL_network and intermedia_network. All DM nodes form resource pool and each node is a vdu.
- LB: Stands for LineCard Module, which links to CTRL_network and intermedia_network and extermedia_network. All LB nodes form resource pool and each node is a vdu.
5.1. 2. vRNC Definition¶
The files dependency and correspoding specificaiton of vRNC definition are shown below: Fig. 5.2
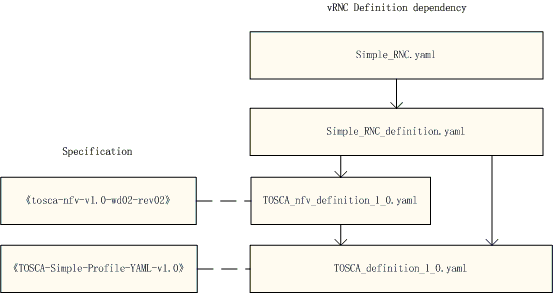
vRNC Definition¶
- TOSCA_definition_1.0.yaml should be the lastest version, which is updated by tosca-parser community, but some keywords (such as substitution_mappings) in the correspoding standard of “TOSCA-simple-profile-YAML-v1.0” is not supported.
- TOSCA_nfv_definition_1.0.yaml is a new file, and not implemented in code, and the correspoding standard of “tosca-nfv-v1.0-wd02-rev02” is not complete now.
