VNF Testing Framework Requirements¶
Introduction¶
This chapter covers comprehensive VNF Conformance requirements for enabling required process and steps to provide VNF badging based on define scope of compliance and validation. This includes end to end test framework requirements, badging entry and exit criteria, profiles to reference, different stake holders and Conformance Methodologies by using certified NFVi under NFVi badging program.
Conformance Methodology¶
It defines the end-end framework and process required for certifying the given VNF.
End-End framework:
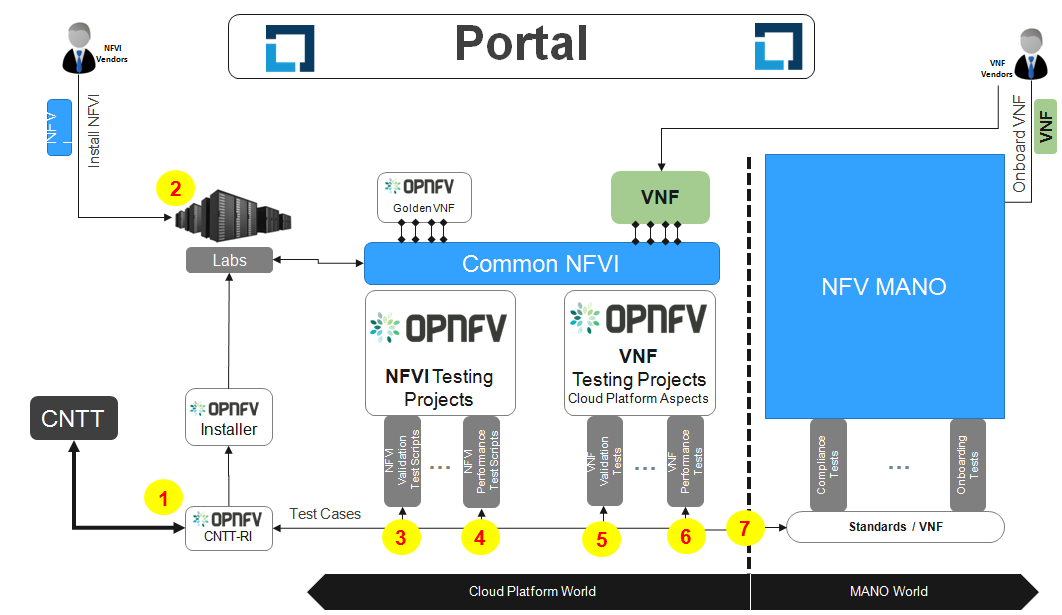
Fig. 10 End-End framework¶
Here, the steps 1-4 are NFVI related steps are covered in detail in NFVI Conformance Requirements.
Step-5. Interoperability validations for VNF functional testing defined.
Step-6. Interoperability validations for VNF performance testing defined (IOPS, connection, threading, resource consumption).
Step-7. Sending requirements to the VNF requirements projects in terms of t-shirt sizes, config settings, required for VNF/orchestration validation.
Conformance flow:
The entry and exit criteria defined in below section are pre-requisities for this flow.
VNF Vendors submit the VNF into OVP Lab for Conformance (Fulfilling the entry criteria is pre-requisities for this step.)
As part of OVP lab, already required test cases, test tools, eco-system like MANO and appropriate certified NFVi to be setup as defined part of entry criteria. This lab could either OVP 3rd party lab or VNF vendors.
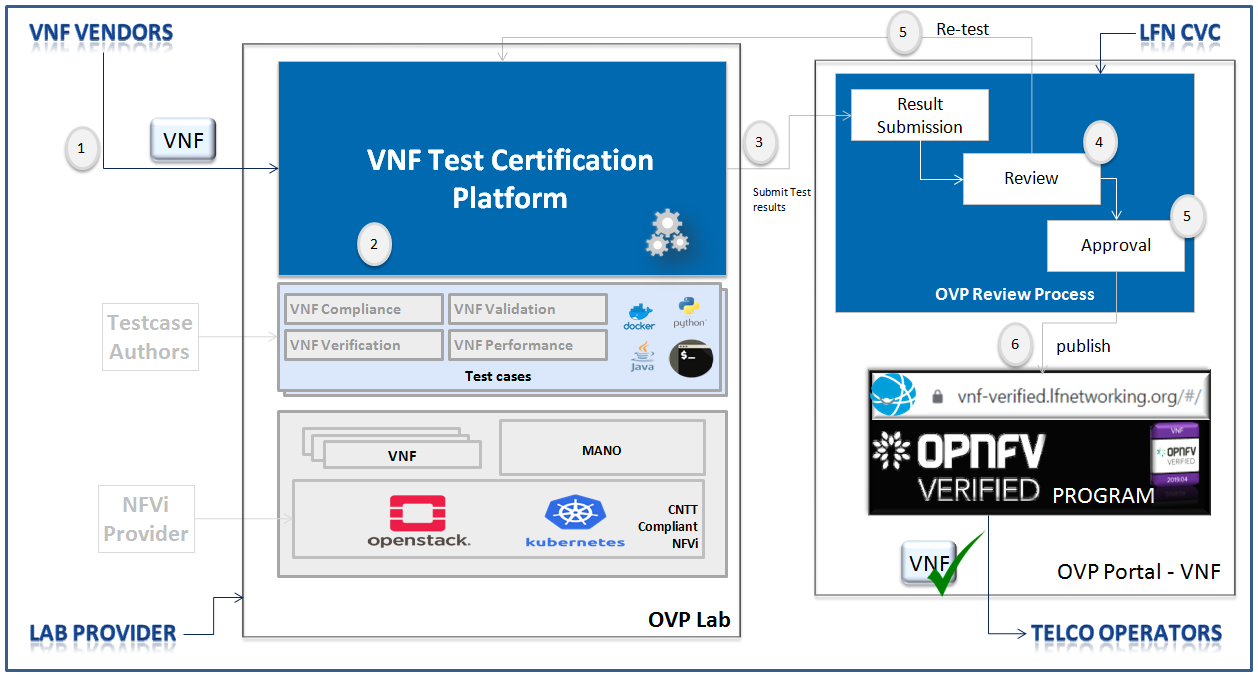
Fig. 11 OVP 3rd party lab¶
Once testing is completed done, test results will be submitted to the OVP portal for community review along with additional information such as product name, documentation links, primary company contact information, etc.
LFN CVC community team reviewers will review the results submitted and will approve or reject it based the details provided.
If reviewer rejected it, then step 2 and 3 will be ran again to address the review comments. Otherwise once reviewer approved it, corresponding VNF will be published into OVP VNF Portal with OVP badge.
- LFN staff will provide the certificate badge graphics and graphical usage guidelines.The OVP portal will reflect LFN’s disposition and assignment of the certified VNF badge.
Now VNF is ready and Telco Operators can start consume it.
Profiles Reference¶
The NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) is the totality of all hardware and software components which build up the environment in which VNFs are deployed, managed and executed. It is, therefore, inevitable that different VNFs would require different capabilities and have different expectations from it. So one of the main targets of Anuket is to define an agnostic NFVI and removes any dependencies between VNFs and deployed Infrastructure (NFVI) and offer NFVI to VNFs in an abstracted way with defined capabilities and metrics. This would help operators to host their Telco Workload (VNF) with different traffic types, behaviour and from any vendor on a unified consistent Infrastructure. so as part of VNF Conformance, its important to certify the VNF based on profiled defined in :doc:ref_model/chapters/chapter02`.
In Workload Requirements & Analysis, following NFVi profiles are proposed as reference:
Basic: for VNF that can tolerate resource over-subscription and variable latency.
Network Intensive: for VNF that require predictable computing performance, high network throughput and low network latency.
Protoype VNFs¶
A portion of the NFVI badging methodology includes Empirical Validation with Reference Golden VNFs (aka CVC Validation) which will ensure the NFVI runs with a set of VNF Families, or Classes, to mimic production-like VNF connectivity. These tests are to 1) ensure interoperability checks pass, and 2) there is an established baseline of VNF behaviors and characters before vendor supplied VNFs are tested and certified. In other words, empirical validations will confirm performance and stability between Platform and VNF, such as validating packet loss is within acceptable tolerances.
Badging Requirements¶
Defined. Badging refers to the granting of a Conformance badge by the OVP to Suppliers/Testers of Anuket NFVI+VNF upon demonstration the testing performed confirms:
NFVI adheres to Anuket RA/RM requirements.
Anuket certified VNFs functionally perform as expected (i.e. test cases pass) on NFVI with acceptable levels of stability and performance.
Following table shows the bading requirements with scope of mandatory (must) or optional.
Requirement id |
scope |
details |
|---|---|---|
CVreq.VNF.001 |
must |
Receive NFVi badge in lab setup per RI-1 standards, performing h/w validations, performing s/w manifest validations, running nfvi compliance, validation, and performance checks |
CVreq.VNF.002 |
must |
met all entry and exit criteria |
CVreq.VNF.003 |
must |
run i nteroperability validations, including instantiation, communication / health, and removal |
CVreq.VNF.004 |
shall |
utilize automation frameworks to run all required tests. Conformance process would improve, if test framework satisfy the required defined in this chapter under VNF Test Conformance platform requirements section |
CVreq.VNF.005 |
must |
pass all required tests |
CVreq.VNF.006 |
must |
prepare release notes, with issues known, their severity and magnitude, mitigation plan |
CVreq.VNF.007 |
must |
publish results in defined normalized output |
CVreq.VNF.008 |
must |
respond /closed badging inquiries |
CVReq.VNF.010 |
optional |
for bading VNF supplier can choose to run their own test h arnesses/suites to validate VNF functional and performance behaviors and performance |
Badging Scope¶
The VNF badging includes:
NFVi Verifications (Compliance): Manifest Verifications will ensure the NFVI is compliant, and delivered for testing, with hardware and software profile specifications defined by the Ref Model and Ref Architecture.
Empirical Validation with Reference VNF (Validation): Empirical Validation with Reference Golden VNFs will ensure the NFVI runs with a set of VNF Families, or Classes, to mimic production-like VNFs to baseline infrastructure conformance.
Candidate VNF Validation (Validation & Performance): Candidate VNF Validation will ensure complete interoperability of VNF behavior on the NFVI leveraging VVP/VNFSDK test suites to ensure VNF can be spun up, modified, or removed, on the target NFVI (aka Interoperability).
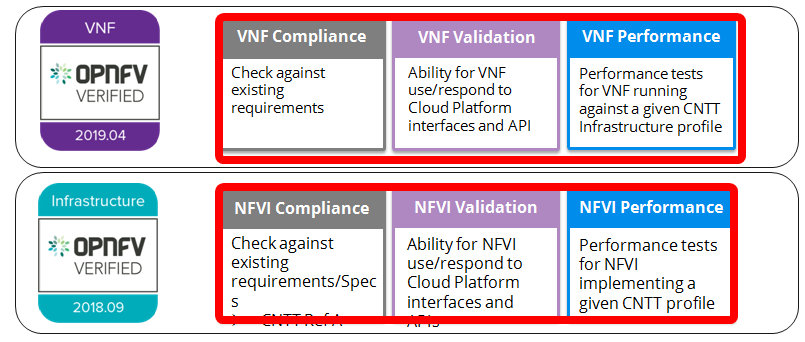
Fig. 12 Candidate VNF Validation¶
Entry criteria¶
Before entering into the VNF badging process, VNF needs to satisfy the following requirements as entry criteria:
Environment Requirements : Published details providing evidence that a RAx compliant lab has been implemented, meeting requirements set forth in respective RM and RAx documentation for features, options, and capabilities needed for VNF test validations. Expected information includes:
Lab Flavor
Component software rev levels
Confirmation of compatibility with external systems
Tenant needs identified
All connectivity, network, image, VMs, delivered with successful pairwise tests
Lab instrumented for proper monitoring
VNF artifact : VNF cloud (native) image, VNF configurations and guidelines, automation scripts, etc
NFVi profiles: List of supporting OVP Certified Anuket compliant NFVi
Completed Security review report
Vendor specific test cases and its deployment and usage guidelines
Exit criteria¶
VNF Conformance testing should be completed with following exit criteria:
All required test cases should be passed
No outstanding high severity issues and other known issues to be documented
Release notes
Provided with required installation guide, configuration guide, etc.
Test results collated, centralized, and normalized, with a final report generated showing status of the test scenario/case (e.g. Pass, Fail, Skip, Measurement Success/Fail, etc), along with traceability to a functional, or non-functional, requirement
VNF Test Conformance platform Requirements¶
Test platform requirements are provided to address test case design, distribution, execution and result reporting along with required artifacts and environments in place and are defined based on below scope.
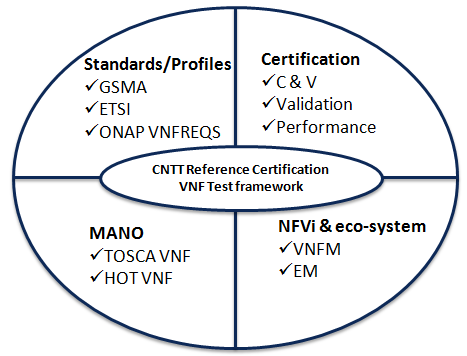
Fig. 13 Test platform requirements¶
Standards/Profiles¶
ETSI (TOSCA)
GSMA
ONAP VNFREQS (HOT)
Test cases¶
Refer chapter RC-06 for more details on test case requirements defined for VNF under Anuket. Platform should support to managed and execute these test cases.
NOTE: For Conformance, only compliance and verification test cases will be considered, but in future, it could be extent to validation and Performance related testing.
Compliance¶
Perform compliance check based on
TOSCA using ETSI SOL004 & SOL001
OpenStack HOT using ONAP VNFREQS
GSMA profile as defined in chapter RM-04.
Verification¶
Perform on-boarding/ verification life cycle operation (from instantiation, configuration, update, termination) using MANO supporting Anuket compliant NFVI.
Validation¶
Perform various VNF type specific functionality operations on Anuket RA & RM compliant NFVI
Performance¶
Perform various performance related testing and facilitate for benchmarking the VNF performance on different profile and scenarios.
Eco-system MANO/NFVI¶
Platform would support to execute various test cases on Anuket RA & RM compliant NFVi along with required MANO system supporting these NFVi.
VNF¶
Suppliers of VNFs/CNFs seeking to receive VNF Conformance badges must first ensure their testing is performed against a compliant RM/RA architecture supporting all capabilities, features, and services defined by the respective RM/RA requirements. More specifically, the VNF Supplier must ensure their implementation of the RM/RA receives the NFVI Conformance badge prior to starting VNF testing. Finally, to receive VNF Conformance, the test platform will need to support TOSCA and HOT based VNF distros.
In addition, Platform should be able to perform the required test case management and executions and produce the result the CVC OVP portal for Conformance process along with required testing foot print details. So overall scoped example architecture could be as below:
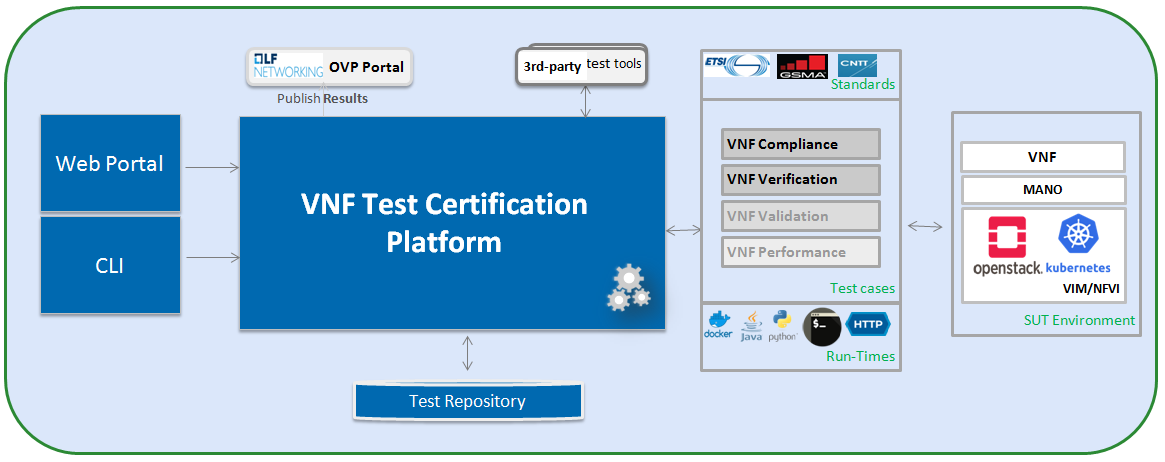
Fig. 14 VNF Test Certification Platform¶
Test Case Model¶
As there are more number of VNF at different levels of networking such as access, transport and core level as well as OSI level L0-L7. Every network function provides set of pre-defined features and functionalities. So its important to model test cases for every functionality to identify it uniquely and use it as part of test flow design.
As part of modeling its very important to capture the following details
Test case Name
Test case description
Virtual Network function Name
Network function Feature/functionality name
Test case input parameters
Test case result attributes
Test case version
while implementing the test cases, this model would act as specification and as it captures the input and output, it would help while designing the test flow which will help to execute set of test cases in pre-defined flow.
Test case management¶
Test case : On-board/discover, update, disable/enable, delete
Test suite : On-board/discover, update, disable/enable, delete
Test flow : design/discover, update, disable/enable, delete
Test Execution management¶
- Run-time: One of the common nature of the test environment is heterogeneous and multiple vendors and open communities would provide various test tool and environment to support execution of test cases developed under different run-times(JVM, Python, Shell, Container, Cloud VM, etc)
RPC: In order to enable the scaling/remote execution, it should be enabled with required RPC support.
When VNF test platform execute the test cases, it captures the footprints of test case execution along with results, which are made available to user and integrated system for consuming.
Test Result management¶
Categorization. Test suites will be categorized as Functional/Platform or Performance based.
Results. Test results reporting will be communicated as a boolean (pass/fail), or Measurements Only.
Functional Pass/Fail signals the assertions set in a test script verify the Functional Requirements (FR) has met its stated objective as delivered by the developer. This will consist of both positive validation of expected behavior, as well as negative based testing when to confirm error handling is working as expected.
Performance-based Pass/Fail determination will be made by comparing Non-Functional (NFR) KPIs (obtained after testing) with the Golden KPIs. Some of the examples of performance KPIs include, but not limited to: TCP bandwidth, UDP throughput, Memory latency, Jitter, IOPS etc.
Measurement Results. Baseline Measurements will be performed when there are no benchmark standards to compare results, or established FRs/NFRs for which to gauge application / platform behavior in an integrated environment, or under load conditions. In these cases, test results will be executed to measure the application, platform, then prepare FRs/NFRs for subsequent enhancements and test runs.
Formats. As part of execution management, system produces the result in JSON format which can be represented in various form like YAML, CSV, Table, etc.
Search & Reporting. Search would help to query the test results based on various fact such as test case, VNF, date of execution, environment, etc. and produce the report in various format like pie-chart, success rates, etc
Collation | Portal. The following criteria will be applied to the collation and presentation of test-runs seeking Conformance:
RA number and name (e.g. RA-1 OpenStack)
Version of software tested (e.g. OpenStack Ocata)
Normalized results will be collated across all test runs (i.e. centralized database)
Clear time stamps of test runs will be provided.
Identification of test engineer / executor.
Traceability to requirements.
Summarized conclusion if conditions warrant test Conformance (see Badging Section).
Portal contains links to Conformance badge(s) received.
Test Artifact management¶
As part of testing various binaries, configurations, images, scripts ,etc would be used during test cases building or execution and Version artifact supports such as VNF CSAR.
Test Scenario management¶
Allow to create repeatable scenario includes test cases, artifacts and profiles.
It helps to create dynamic testing scenario development and testing from the existing test cases and flows along with required artifacts and profiles. It allows to run repeated testing with one or different profiles.
Test Profile management¶
For every test case execution needs to be configured with required environments and predefined test input parameter values. This is provided by means of profile
Profile should be having option to include other profiles to manage the hierarchy of them.
As part of profile, testing environment URL, credentials and related security keys are captured and while running the test cases, user would be able to inputs the required profile in place of actual inputs and artifacts.
Also helps in Managing System under test configuration and multiple MANO / NFVI and related eco system management elements.
Tenant & User management¶
Testing involves design, distribution by different user roles and executed across multiple tenant’s environments.
Conformance management & integration¶
Platform should have integration with OVP Conformance portal for submitting results with OVP defined format.
It should enable repository of certified VNFs which can be used for testing validation and performance.
User & System interfaces¶
User interface:
CLI
Web portal
Programming interface:
REST API
gRPC
Deliverables¶
Platform should be able to get deployed in both container and cloud environments. so following model deliverables would enable it:
Docker image based installation
Standalone installation scripts and zip artifact
VNF Test Cases Requirements¶
Rationale¶
Network functions virtualization (NFV) and softwaredefined networking (SDN) offer service providers increased service agility, OpEx improvements, and back-office automation. Disaggregation, the approach of decoupling the various layers of the stack, from hardware, to NFVI/VIM software, to dataplane acceleration, SDN controllers, MANO components, and VNFs, enables multi-vendor deployments with best-of-breed options at each layer.
The Anuket specifications define the required architecture and model for NFVI which will help to decouple the various commercial product layers and it is important to define and certify the VNF and NFVI. Therefore, in addition to verify general NFVI capabilities based on Anuket RM/RA/RI, it is also necessary to verify that VNFs can provide virtualization functions normally based on the Anuket-compliant NFVI. So the VNF testing should at least include: Compliance,verification,validation,Performance. With the improvement of specifications, the types of tests may continue to add in the future.
In this chapter, the scope and requirements of VNF test cases are defined as reference for VNF Conformance, which helps to perform the various compliance and verification (C&V) testing and submit results to LFN OVP Conformance portal.
Assumptions¶
Here lists the assumptions for VNF Conformance: - NFVI is ready and it should be an Anuket-compliant NFVI - VNF template is ready to deploy and certificate - VNF Test environment is ready, the test environment contains test functions and entities(NFVI, MANO, VNF Test Platform, VNF Test Tools) to enable controlling the test execution and collecting the test measurements. - VNF Test Platform has been integrated with CICD chain - VNF test result can be generated with OVP defined format
Developer Deliverables¶
This section define the developer Deliverables (artifacts),the following list the expectations and deliverables we expect from developers in order to achieve the VNF Conformance: - VNF test cases model/scripts/programs - VNF test cases configuration/profile - VNF test tools
Requirement Type¶
VNF test cases are used to verify whether the virtualization network functions can be deployed on the Anuket-compliant NFVI and provide normal functions and meet performance, security and other requirements.
By running these VNF test cases and analysis the test results, can be used for VNF compliance, verfication,validation and performance Conformance and help on Anuket-compliant NFVI validation and performance Conformance.
All the VNF test cases should be supported and run by VNF E2E Conformance and verification Framework and generate outputs, logs to identify whether the test passed or failed.
Anuket defines the following four category testing which should be consistent with the VNF test category defined by OVP.
VNF Test Case Category |
Requirement Number |
Type (Measu rement/Boolean) |
Definit ion/Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Compliance |
VNF.COMPreq.001 |
Boolean ( i.e. Pass/Fail) |
Test case “must”perform a platform check against the Open Stack requirements and VNF package structure and syntax requirements |
Verification |
VN F.VERIFYreq.001 |
Boolean ( i.e. Pass/Fail) |
Test case “must” perform on-boarding/ verification life cycle operation validation |
Validation |
V NF.VALIDreq.001 |
Boolean ( i.e. Pass/Fail) |
Test case “must” perform API validation tests to verify operability |
Performance |
VNF.PERFreq.001 |
Measurement |
Test case “must” execute various performance related testing and facilitate for benchmarking the VNF performance on different profile and scenarios |
Note: The four category testing can be gradually supported and in the future, will also cover secutiry and other test category.
Interaction Type¶
Describe the types of Interactions: Extended Topology, Complex (Akraino), Functional, HA, Fault, Interoperability
Performance Profiles¶
Performance profiles are not in the scope of current release, and in future it would need to align with chapter RM-4 defined measurements.
VNF Class/Family and Characteristics¶
Describe and provide a Table of VNF Class/Family & Characteristics of Each
The communication network usually consists of three parts: access network, transmission network/bearer network and core network. Following are some examples of network elements for each type of network
Network Type |
Network Elements |
|---|---|
Access Network |
Including mobile access network, wireless access network, wired access network |
Transport network & Bearer network |
Including Trunk Optical Transport Network,Metro transport network,IP backbone network, etc. |
Core Network |
Circuit domain, including MSC / VLR, GMSC, MGW, NPMSC, HLR / AUC, NPHLR, HSS,etc;Packet domain devices, including MME, SAE GW, EPC CG, EPC DNS, PCC,etc;Core network equipment for IoT private network,including PGW/ GGSN、PCRF、HSS/HLR,etc;5G core network element,including AMF、SMF、UPF、UDM/UDR/AUS F、PCF、NSSF、NRF、SMSF,etc |
In addition to the above network elements, there are some other data communication network element, including FW, DNS, Router, GW, etc|
According to the current level of the entire network virtualization, the core network already has many VNFs, and also includes some datacom-type(data communication) VNFs.
We can also classify VNFs based on the level of VNF operation:
VNFs that operate at Layer 2 or Layer 3 are primarily involved in switching or routing packets at these layers. Examples include vRouter, vBNG, vCE device, or vSwitch.
VNFs that operate at Layer 4 through Layer 7 and are involved in forwarding, dropping, filtering or redirecting packets at Layer 4 through 7. Examples include vFirewall, vADC, vIDS/vIPS, or vWAN Accelerator.
VNFs that are involved in the dataplane forwarding through the evolved packet core.
Measurement¶
As part of Conformance testing, following measurement would help for evaluating the badging:
VNF type defined as part of Chapter RM-02 and its profile used for testing.
Test cases and their test results including the test case outputs, logs
VNF model type (TOSCA/HOT)
Test case pass/failed
Different NFVi profiles used and LAB reference identifier
Test owner (point of contact)
VNF Test Cases¶
Compliance test cases¶
Currently, there VNFs can be packaged as HEAT templates or in a CSAR file using TOSCA and OVP has supported the VNF compliance test cases(compliance check based on TOSCA using ETSI SOL004 & SOL001;OpenStack HOT using ONAP VNFREQS;GSMA profile), all the OVP supported test case can be found in the following two link:
Test Cases |
Link |
|---|---|
Heat Test Cases |
https://onap.readthedocs.io/en/latest/submodules/vnfrqts/testcases.git/docs/Appendix.html#list-of-requirements-with-associated-tests |
Tosca Test Cases |
https://onap.readthedocs.io/en/latest/submodules/vnfsdk/model.git/docs/files/csar-validation.html |
Above compliance test cases defination can be found https://github.com/onap/vnfsdk-validation/tree/master/csarvalidation/src/main/resources/open-cli-schema
In order to adapt Anuket specification, more compliance test case will be added here.
Verification test cases¶
In general, the VNF Manager, in collaboration with the NFV Orchestrator, the VIM and the EM, is responsible for managing a VNF’s lifecycle. The lifecycle phases are listed below:
VNF on-boarding, it refers to VNF package onboarding to service/resouce Orchestrator
VNF instantiation, once the VNF is instantiated, its associated VNFCs have been successfully instantiated and have been allocated necessary NFVI resources-
VNF scaling/updating, it means the VNF can scale or update by allocating more or less NFVI resources
VNF termination, any NFVI resources consumed by the VNF can be cleaned up and released.
OVP has also supported the lifecycle test case:https://wiki.lfnetworking.org/display/LN/VNF+Validation+Minimum+Viable+Product?src=contextnavpagetreemode
Validation Test cases¶
From the current situation of operators, there are usually corresponding functional test specifications for each types of VNFs. Therefore, different types of VNFs have different functional test cases. Normally, functional tests for VNFs require the cooperation of surrounding VNFs. Or use the instruments to simulate the functions of surrounding VNFs for testing. Therefore, different test cases need to be defined according to different types of VNFs
Performance Test cases¶
This is the same as what described in validation test cases,the performance test cases need to be defined according to different types of VNFs. Combined with the classification of VNF, according to the protocol level that VNF operates, it can include:
VNF data plane benchmarking, like forwarding Performance Benchmarking,Long duration traffic testing, low misrouting and so on.
VNF control plane benchmarking, like throughput
VNF user plane benchmarking, like Packet Loss,Latency, Packet Delay
ETSI spec has also defined the testing method http://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gs/NFV-TST/001_099/001/01.01.01_60/gs_nfv-tst001v010101p.pdf